Figure 1.
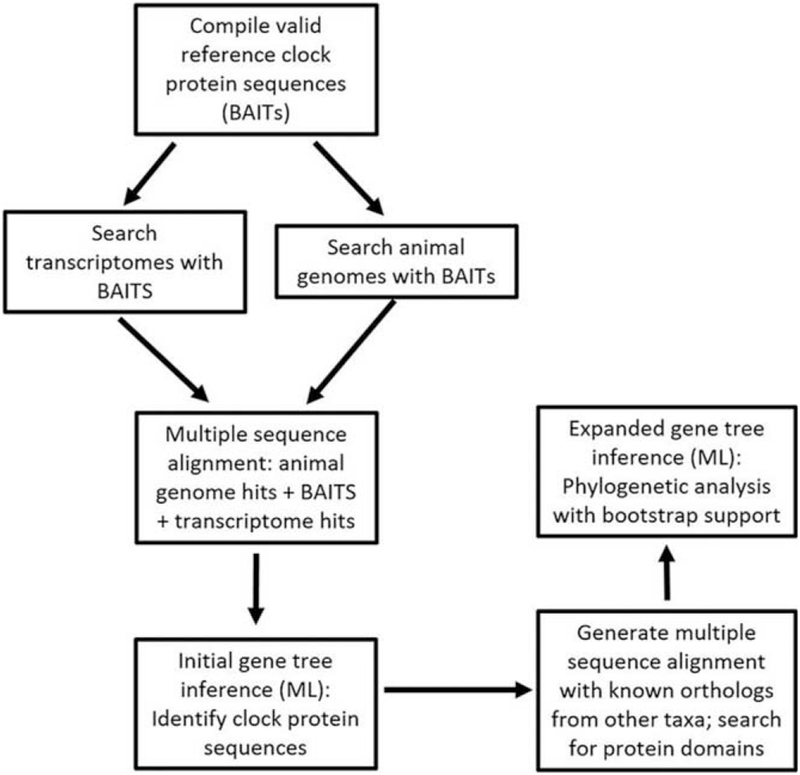
Schematic flow diagram of the steps taken to sequence and compare clock proteins. The creation of a bioinformatic pipeline significantly increased the efficiency with which contiguous sequences from the nudibranch transcriptomes could be identified as potential gene orthologs; more importantly, it accurately determined whether they were most closely associated with the products of specific clock genes or more similar to structurally related proteins that do not serve a circadian clock function. To begin, valid reference clock protein sequences (what we termed “BAIT” sequences) were compiled and used to fish out contiguous sequences from the nudibranch transcriptome assemblies. After aligning all sequences, contiguous sequences were then mapped on a phylogenetic tree with the BAIT sequences as well as closely matched protein sequences from automated BLAST searches. This enabled us to identify putative clock protein sequences from each nudibranch transcriptome. ML, maximum likelihood.
