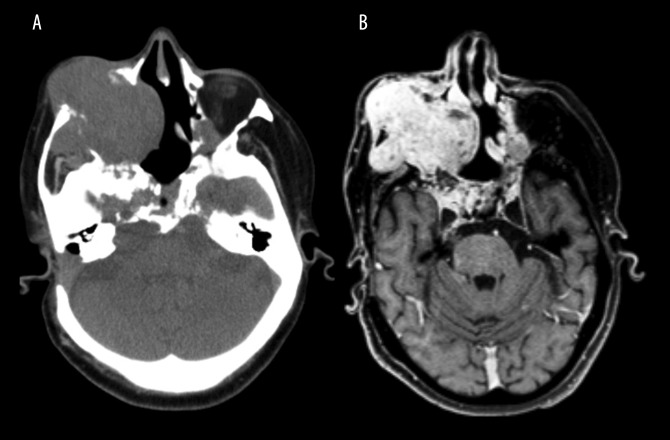
Figure 1.
Computed tomography (CT) and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) shows an infiltrative and expansive lesion arising in the clivus. (A) Axial slice of a computed tomography (CT) scan showing an expansive, infiltrative, lobulated, and heterogeneous lesion. The lesion is centered on the clivus and extends to the right maxilla, right maxillary sinus, and the soft tissues of the zygomatic region. The clivus is a depression in the anterior basilar occipital bone of the skull base, posterior to the dorsum sellae, at the junction with the sphenoid bone. (B) Axial slice of a contrast-enhanced (gadolinium), T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with multiplanar acquisition shows an infiltrative and expansive lesion with cystic areas and adjacent calcified material. Signs of previous surgical treatment are present.