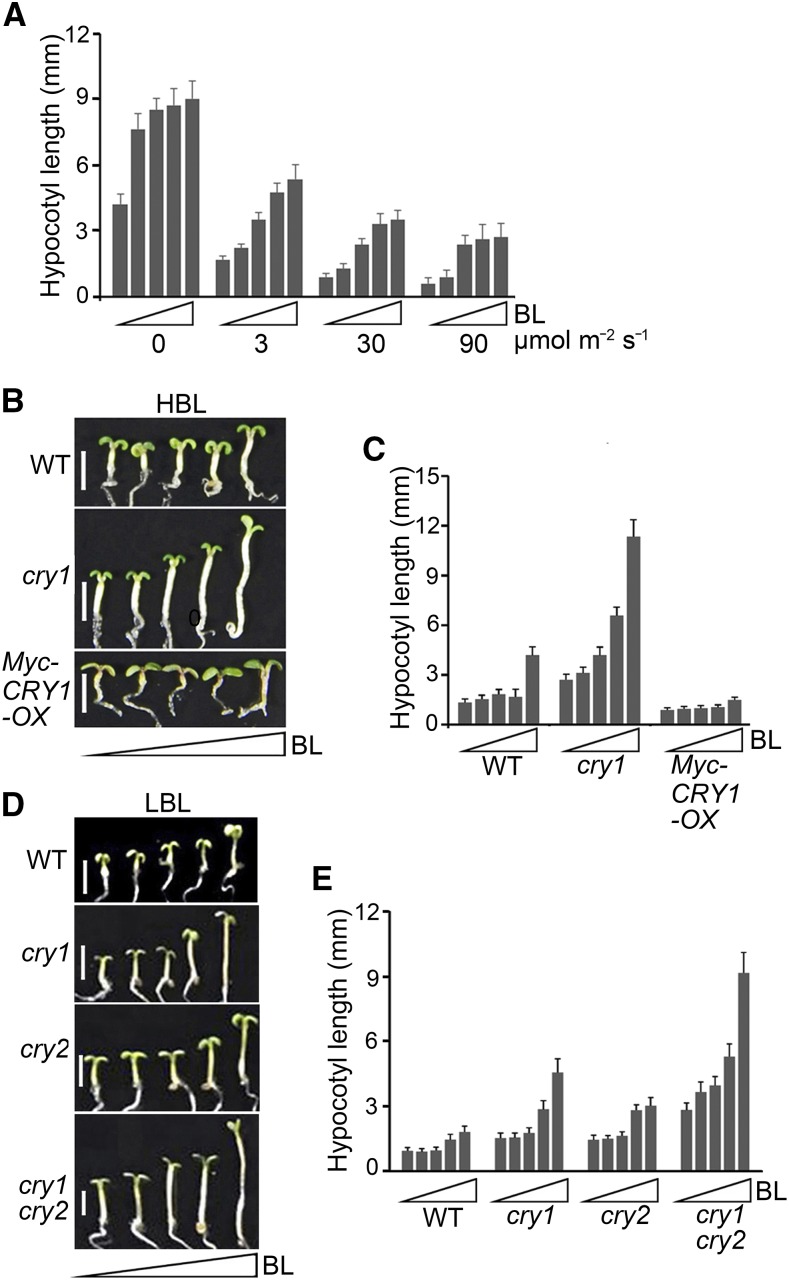
Figure 3.
CRYs Are Involved in Mediating the Inhibition of BR Responses in Arabidopsis Seedlings in Response to Blue Light.
(A) Analysis of blue light inhibition of BR responses. Wild type seedlings were grown for 6 d on 0.5× MS plates supplemented with 2 μM BRZ plus a gradient of concentrations of BL (small triangles represent 0, 1, 10, 100, and 1000 nM) in the dark and increasing intensities of blue light (0, 3, 30, and 90 μmol m−2 s−1), and then hypocotyl length was measured. Three independent experiments were performed, with similar results.
(B) and (C) Analysis of the involvement of CRY1 in the inhibition of BR responses by high-intensity blue light (HBL). Wild-type, cry1, and Myc-CRY1-OX seedlings were grown on the same medium as in (A) in blue light (30 μmol m−2 s−1) for 6 d (B), and hypocotyl length was measured (C). Triangles represent concentration gradients of BL from 0 to 1000 nM. Bars in (B) = 2.5 mm. Two independent experiments were performed, with similar results.
(D) and (E) Analysis of the involvement of CRY1 and CRY2 in the inhibition of BR responses by low-intensity blue light (LBL). Wild-type, cry1, cry2, and cry1 cry2 seedlings were grown on 0.5× MS plates supplemented with 2 μM BRZ plus gradient concentrations of BL (0, 1, 10, 100, and 1000 nM) under low-intensity blue light (5 μmol m−2 s−1) for 5 d (D), and hypocotyl length was measured (E). Triangles represent concentration gradients of BL from 0 to 1000 nM. Bars in (D) = 2.5 mm.
Data in (A), (C), and (E) are means ± sd (n > 20 seedlings per treatment and genotype).