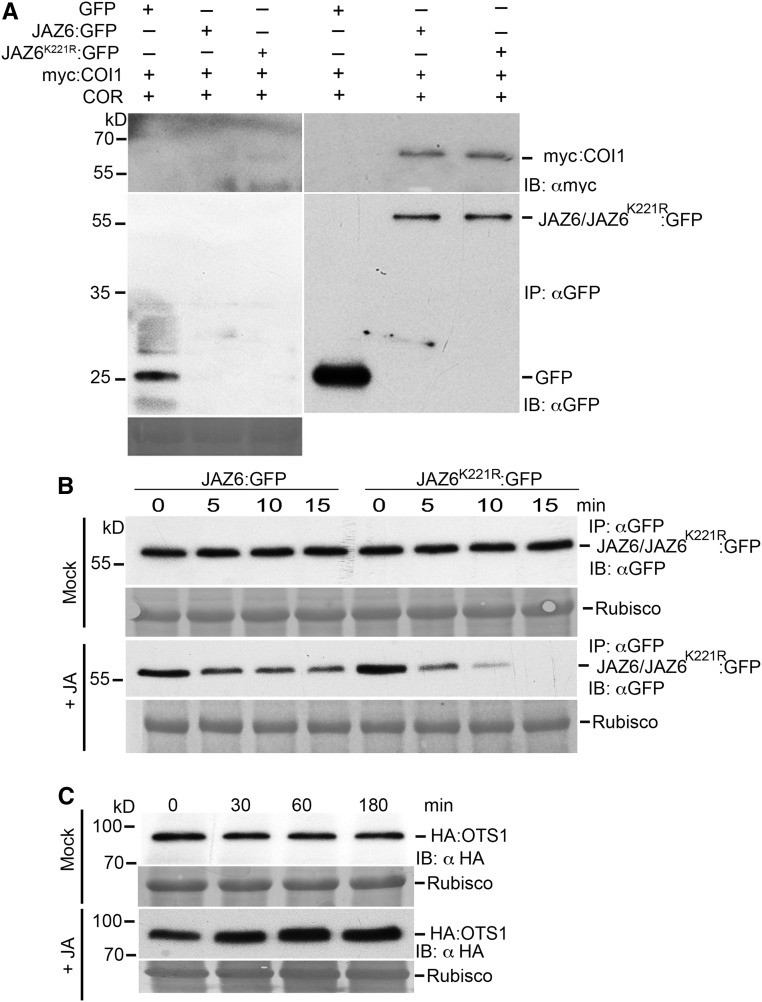
Figure 4.
JAZ6 SUMO Site Mutation Affects the Stability of JAZ6 Protein but Does Not Affect Its Interaction with COI1.
(A) Coimmunoprecipitation of myc:COI1 with GFP only, JAZ6:GFP, and JAZ6K221R:GFP was performed in planta using N. benthamiana transient assays to investigate the interaction of JAZ6:GFP and JAZ6K221R:GFP with myc:COI1 protein. Immunoprecipitates (IP: αGFP) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblots were probed with αGFP to detect JAZ6:GFP and JAZ6K221R:GFP and GFP alone and with αmyc to detect myc:COI1 proteins. Ponceau staining indicating Rubisco levels was employed to determine protein loading for the immunoprecipitation (IP:αGFP).
(B) JA-mediated degradation of JAZ6:GFP and JAZ6K221R:GFP proteins. Immunoblot probed with anti-GFP antibodies showing protein levels of 35S::JAZ6:GFP and 35S::JAZ6K221R:GFP in respective seedlings treated with and without (mock treatment) JA (100 µM). Seedling samples were collected at the indicated time points. Ponceau staining indicating Rubisco levels was employed to determine protein loading for the immunoprecipitation (IP:αGFP).
(C) Immunoblots probed with αHA (IB: αHA) indicating the accumulation of HA:OTS1 protein in 12-d-old seedlings expressing 35S promoter driven HA-OTS1 transgene. Seedlings were treated with and without (mock) JA. Protein samples from seedlings were collected at the indicated time points. Ponceau red-stained Rubisco protein was used to indicate total protein levels.