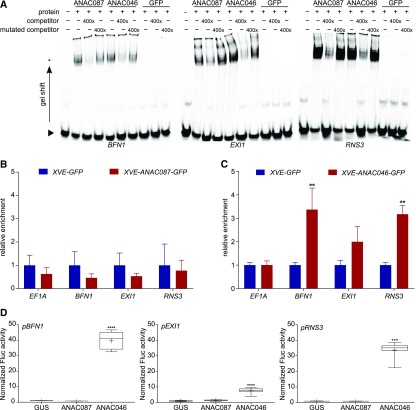
Figure 4.
BFN1, EXI1, and RNS3 Are Indirect Targets of ANAC087 and Direct Targets of ANAC046.
(A) EMSA for binding of ANAC087 and ANAC046 HIS6MBP-tagged proteins to labeled 40-bp promoter fragments of BFN1, EXI1, and RNS3. Both proteins caused a slower migration of the protein-probe complex (band shift indicated by an asterisk) compared with the free probe (indicated by arrowhead). When a 400× concentrated unlabeled competitor probe was added, the signal of the protein-probe complex decreased, whereas when a mutated, unlabeled competitor probe was added, the signal intensity was restored, indicating the specificity of the interaction. When the negative control HIS6MBP-labeled GFP or no protein was added, no band shift was observed.
(B) and (C) ChIP-qPCR analysis showed no enrichment of BFN1, EXI1, or RNS3 promoter fragments when ANAC087-GFP was immunoprecipitated. However, when ANAC046-GFP was pulled down, promoter fragments of BFN1, EXI1, and RNS3 were enriched, as detected by RT-qPCR. The graph shows relative enrichment compared with estradiol induced pRPS5A:XVE>>GFP seedlings. As a negative control, the housekeeping gene EF1A was used, which did not show enrichment. Error bars indicate se of four biological replicates (protein extractions from four independently grown samples). t test; **P < 0.01.
(D) TEAs show increased activity of firefly luciferase (Fluc) from the 2-kb promoters of pBFN1, pEXI1, and pRNS3 when ANAC046 was present, indicating that ANAC046 was able to activate transcription from these promoters. ANAC087 was not able to induce promoter activity of pBFN1, pEXI1, or pRNS3. As a negative control, GUS was used, which is not able to induce transcription. Activation is shown relative to GUS. Box plot whiskers indicate maximum and minimum values; + indicates mean of eight biological replicates (eight independent protoplast transformations). Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric test ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001.