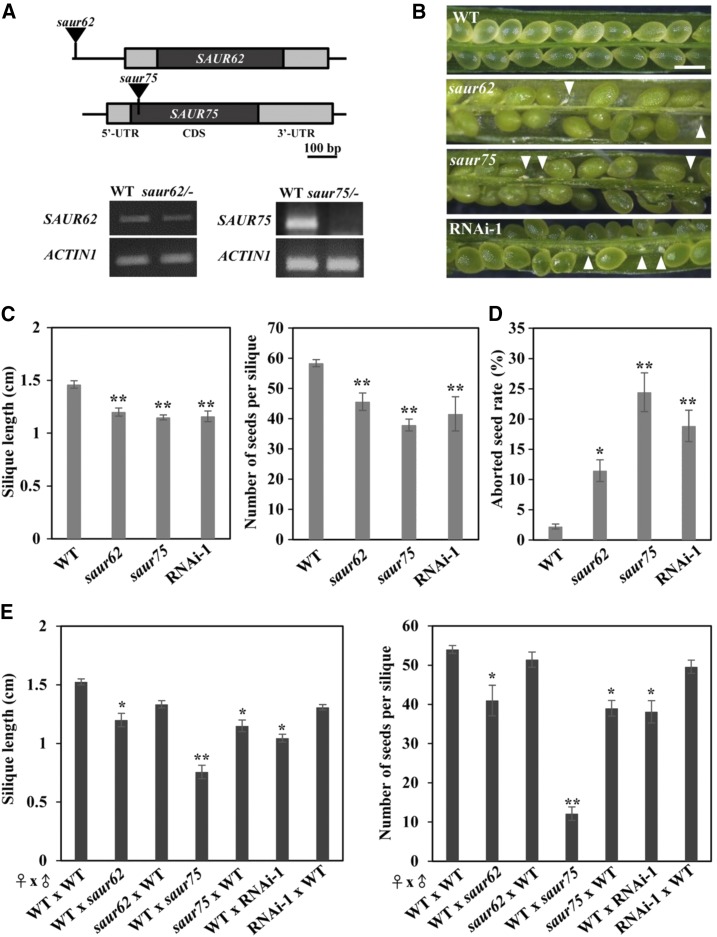
Figure 3.
Mutations and knockdown expression of SAUR62 and SAUR75 significantly impair fertility. A, Schematics of the genomic fragments of SAUR62 and SAUR75 with the corresponding T-DNA insertion sites marked by black triangles. RT-PCR analysis showed that saur62/− was a knockdown mutant and saur75/− was a null mutant. ACTIN1 was used as an internal loading control. B and C, Effects of mutations of SAUR62 and SAUR75 on fertility. B, Aborted seeds (white arrowheads) in dissected siliques. Bar = 0.5 mm. C, Length and average seed number per mature silique obtained from the primary shoots of wild-type (WT), saur62, saur75, and RNAi-1 plants. Columns represent means ± se (n > 20). Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type (**, P < 0.01) by Student’s t test. D, Frequencies (%) of aborted seeds per silique of wild-type, saur62, saur75, and RNAi-1 plants. Columns represent means ± se (n > 30). Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type (*, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.01) by Student’s t test. E, Silique length and number of seeds per silique in reciprocal pollination plants. Columns represent means ± se (n > 10). Asterisks indicate significant differences from wild-type ♀ × wild-type ♂ (*, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.01) by Student’s t test.