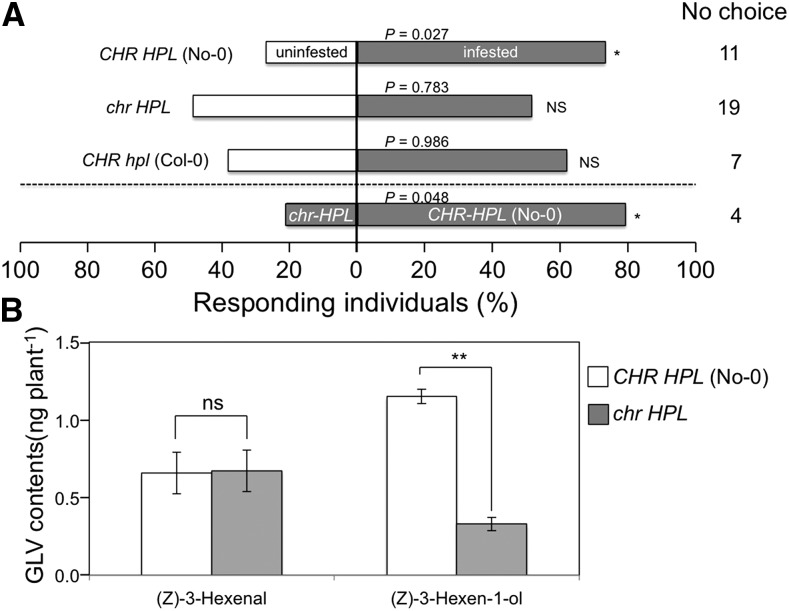
Figure 6.
Role of CHR in C. vestalis flight responses and in volatile emission following P. xylostella infestation. A, Flight responses of C. vestalis to P. xylostella-infested (gray) and uninfested (white) Arabidopsis CHR HPL (No-0), chr HPL, and CHR hpl (Col-0) plants (40 individuals; above the dashed line) and to P. xylostella-infested chr HPL and CHR HPL (No-0) plants (60 individuals; below the dashed line). *, 0.05 > Ptotal > 0.01 (replicated G test); NS, no significant difference. C. vestalis that did not choose either plant (no-choice subjects) were not included in the statistical analysis. B, (Z)-3-Hexenal and (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol emissions from wild-type (No-0, CHR HPL) and mutant (chr HPL) plants after a 24-h infestation with P. xylostella larvae. The quantities of volatiles in headspaces of glass vials containing three plants were collected after a 24-h infestation period using solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fibers for 30 min. Data are presented as averages ± se (n = 3). **, P < 0.01, as identified using Student’s t test; ns, no significant difference. Quantities of (Z)-3-hexen-1-yl acetate were below the detection limit (less than 0.8 ng in the pot).