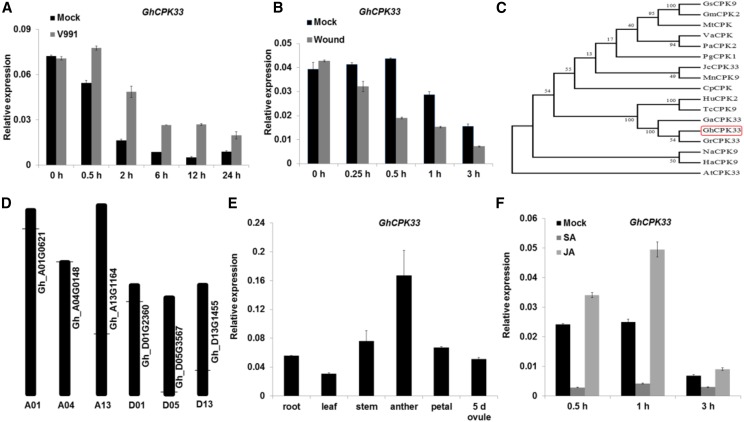
Figure 1.
Identification and expression profile of GhCPK33. A, Reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis of GhCPK33 expression at different time points following inoculation with V. dahliae. Total RNA was extracted from the roots of mock and V. dahliae-inoculated plants. The values are means ± sd, n = 3, and normalized to those of GhUB7. B, RT-qPCR analysis of GhCPK33 expression at different time points following mechanical wounding. The values are means ± sd, n = 3, and normalized to those of GhUB7. Total RNA was extracted from the roots of mock and mechanically wounded plants. C, Phylogenetic analysis of GhCPK33 and CPKs from other plants: Glycine soja (Gs), Glycine max (Gm), Medicago truncatula (Mt), Vitis amurensis (Va), Prunus avium (Pa), Panax ginseng (Pg), Jatropha curcas (Jc), Morus notabilis (Mn), Carica papaya (Cp), Herrania umbratica (Hu), Theobroma cacao (Tc), Gossypium arboreum (Ga), Gossypium raimondii (Gr), Gossypium hirsutum (Gh), Nicotiana attenuata (Na), Helianthus annuus (Ha), and Arabidopsis thaliana (At). The neighbor-joining tree was constructed using the MEGA5 program. D, Distribution of GhCPK33 genes in the whole genome. There are six copies of GhCPK33 in the cotton genome, and the horizontal lines indicate the relative position of each copy on the chromosomes. E, RT-qPCR analysis of GhCPK33 in different tissues. Total RNA was isolated from roots, leaves, stems, anthers, petals, and 5-d ovules of the wild-type cotton cv YZ1. The values are means ± sd, n = 3, and normalized to those of GhUB7. F, RT-qPCR analysis of GhCPK33 expression in JA- and SA-treated cotton. Total RNAs were extracted from the roots of mock and JA or SA-treated plants. The values are means ± sd, n = 3, and normalized to those of GhUB7.