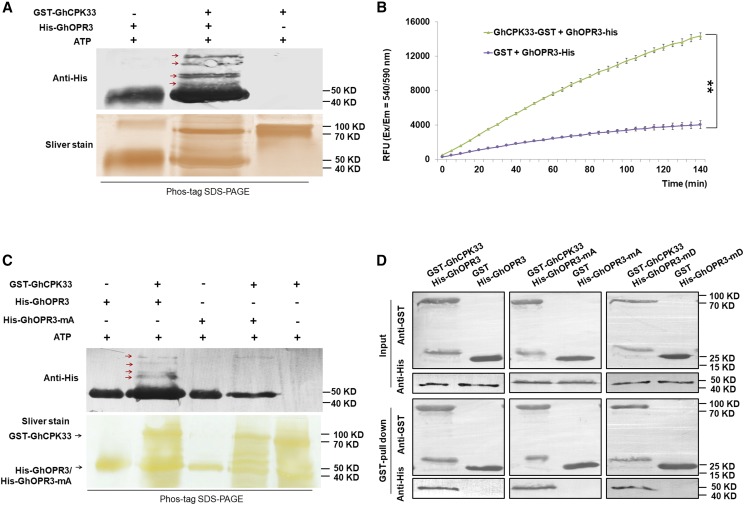
Figure 4.
GhCPK33 phosphorylates GhOPR3. A, In vitro phosphorylation assays between GhOPR3 and GhCPK33 using Phos-tag SDS-PAGE. GST-GhCPK33 was used to phosphorylate purified His-tagged GhOPR3 protein. The reaction mixtures without kinase or without substrate were used as controls. The reaction mixtures were subjected to SDS-PAGE with Phos-tag, and the phosphorylated protein was immunoblotted with anti-His antibody. The red arrows indicate phosphorylated GhOPR3. B, Measurement of GhCPK33 kinase activity using GhOPR3 as a substrate. GST indicates the purified mixture from pGEX-4T-1 without the GhCPK33 DNA insertion and served as the negative control for GST-GhCPK33. The values are means ± sd, n = 3. Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t test: **, P < 0.01. All the experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results. C, In vitro phosphorylation assays of recombinant GhOPR3 or GhOPR3-mA (the Thr-246 site was mutated to Ala) by GhCPK33 using Phos-tag SDS-PAGE. The red arrows indicate phosphorylated GhOPR3. D, GST pull-down assay showing direct interactions between GST-GhCPK33 and His-OPR3, His-GhOPR3-mA, or His-GhOPR3-mD (the Thr-246 site was mutated to Asp) fusion proteins. His-tagged protein was incubated with immobilized GST or GST-GhCPK33 proteins, and the immunoprecipitated fractions were detected by an anti-His antibody or anti-GST antibody. All the experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results.