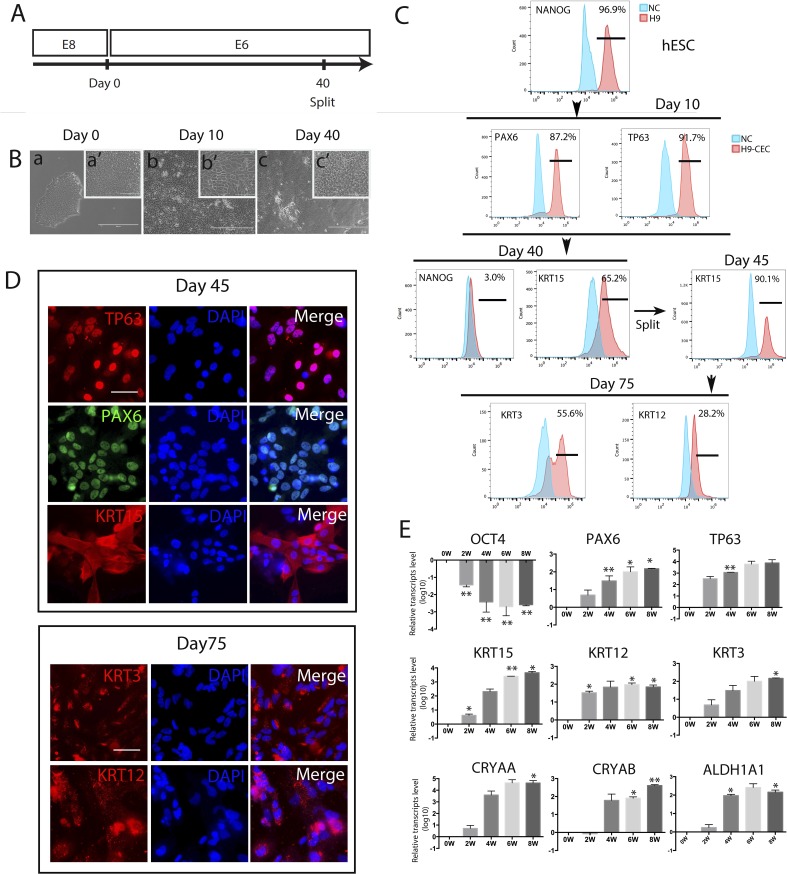
Figure 1.
Generation, characterization, and differentiation efficiency of hESC-derived CEC. CEC were derived from H9 hESC, and three biological replicates were set up for each sample, and each experiment was repeated at least twice (the same hereafter unless stated otherwise). (A) A schematic showing the protocol for hESC differentiation into CEC in E6 with the cells split at day 40. (B) Morphology of the differentiated cells at days 10 and 40. Scale bar: 400 μm (a, b, c) and 100 μm (a', b', c'). (C) Flow cytometry analyses for the pluripotency marker NANOG, the corneal developmental markers PAX6, TP63, and KRT15, and the mature CEC markers KRT3 and KRT12 in hESC that differentiated in E6 for the designated times. (D) Immunostaining for TP63, PAX6, and KRT15 at day 45 of differentiation, and KRT3 and KRT12 at day 75. Scale bar: 50 μm for all images. (E) Real-time PCR analysis for expression of marker genes for pluripotency, CEC progenitors, and mature CEC, and transparency-associated genes during hESC differentiation to CEC for 8 weeks.