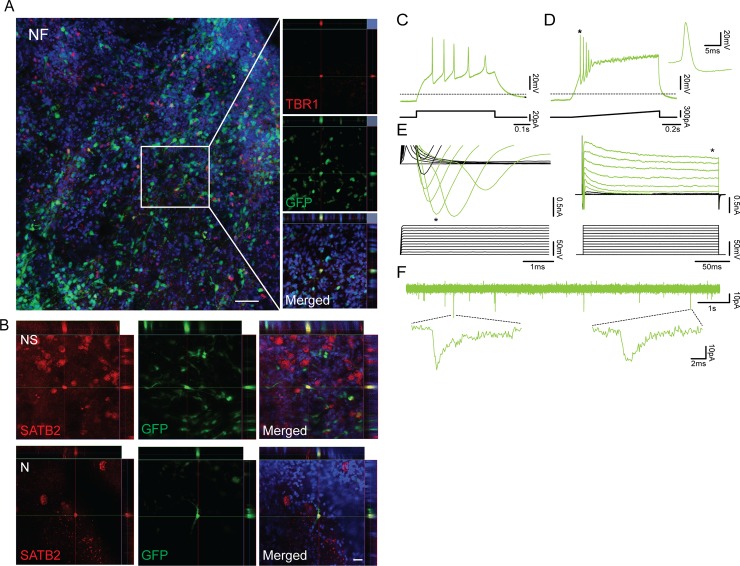
Fig 6. Human ES-iN cells derived by tree TF combinations integrate into adult human cortical tissue.
(A) Confocal image showing an overview of NF-derived hES-iNs plated onto adult human cortical slices (left) and orthogonal projections of confocal images showing expression of the deep-layer cortical neuronal marker TBR1 (right). Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Orthogonal projections of confocal images showing expression of the upper-layer cortical neuronal marker SATB2 in N- and NS-derived hES-iNs. Scale bar: 20 μm. (C) Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from NF-derived hES-iNs at 5 weeks after transplantation onto hCtx organotypic slices (n = 7). Voltage traces illustrating the N-derived hES-iNs’ ability to generate APs during a 20 pA current step from a holding potential of -70mV. (D) Voltage trace illustrates APs generated during a current ramp from 0-300pA. * indicates expanded APs. (E) Expanded current traces illustrate the inward sodium current (left, denoted by *) and the outward sustained potassium current (right, denoted by *) activated during voltage steps ranging from -70 mV to +40 mV in 10 mV steps. (F) Current trace illustrates the presence of spontaneous downward deflecting currents.