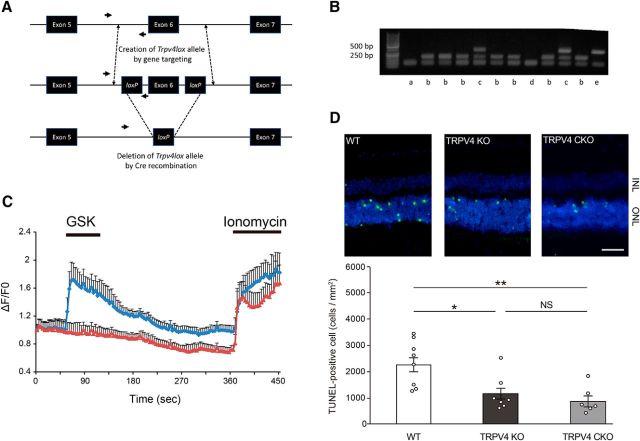
Figure 6.
Müller glial TRPV4 activation accelerates photoreceptor cell death in RD. A, Genetic manipulation of the Trpv4 gene allowing conditional deletion of its sixth allele. The top row shows the wild-type locus. Arrows show the sequence targeted by the primers for the genotyping PCR. The middle row shows the targeted Trpv4 gene, with the exon 6 flanked by loxP recombination sites. The bottom row shows the disrupted gene after Cre recombination. B, PCR genotyping of blank (a; showing a nonspecific band), Trpv4w/w (b; 188 bp fragment), Trpv4wt/lox (c; 188 and 327 bp fragments), Trpv4−/− (d; KO allele where the reverse primer site is not present), and Trpv4lox/lox (e; 327 bp fragment). C, Müller glia/astrocyte-specific TRPV4 conditional KO mice (TRPV4CKO) were generated by crossing hGFAP-Cre mice with TRPV4-flox mice. Shown are representative traces of [Ca2 +]i changes in cultured Müller glial cells (blue diamond line, WT, n = 58 cells; red triangle line,TRPV4CKO, n = 46 cells). Four days after culture, [Ca2+]i changes were measured by Fluo-4 AM. The data were quantified as ΔF/F0. A TRPV4 agonist (10 nm GSK) was applied during recording. At the end of each experiment, we applied ionomycin (5 μm) to identify the surviving cells. D, Representative images of TUNEL staining in RD retinal tissues (WT, TRPV4KO, and TRPV4CKO). Conventional TRPV4KO mice showed significantly less photoreceptor cell death than WT mice 24 h after retinal detachments (*p = 0.06706, n = 7 or 8 eyes). The TRPV4CKO mice showed significantly less photoreceptor cell death than WT mice (**p = 0.020863, n = 6 eyes). The TRPV4CKO results were perfectly matched with those in TRPV4KO, indicating that Müller glial TRPV4 activation accelerates photoreceptor cell death in RD. ONL, Outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer.