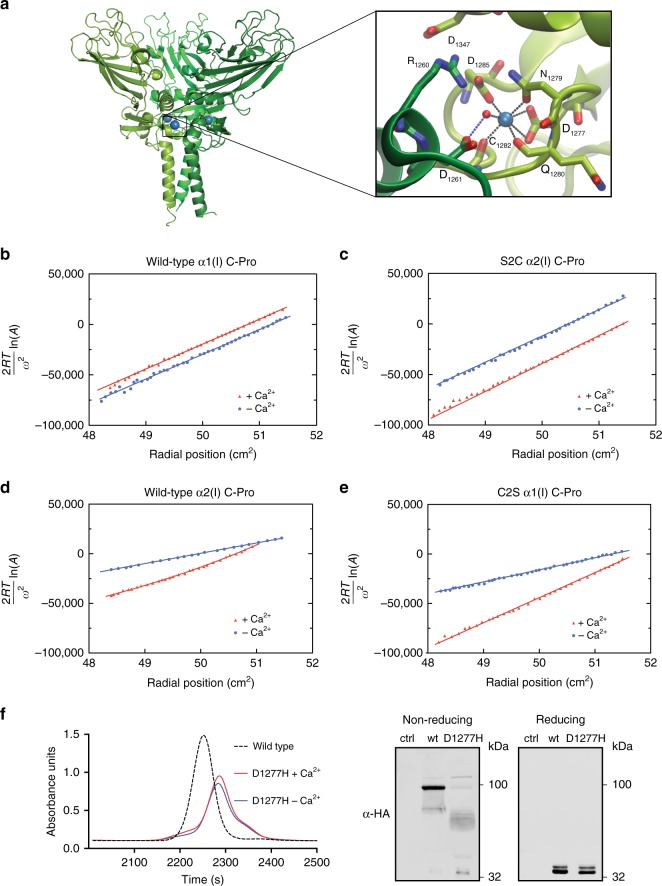
Fig. 4.
The essential role of Ca2+ in templating non-covalent C-Pro assembly. a Crystal structure of C-Proα1(I) (PDBID 5K31)16, highlighting the presence of a Ca2+ ion at each subunit interface of the homotrimer. Each subunit is colored in a different shade of green with Ca2+ ions in blue. Inset: residues involved in binding Ca2+. In b–c, the slopes are directly proportional to the weight average molecular weight at each point. b Sedimentation equilibrium data showing that wild-type C-Proα1(I) is best fit as a single homotrimeric species in the absence of Ca2+ (blue) and in the presence of Ca2+ (red). The best fit is shown as a solid line. c Sedimentation equilibrium data showing that S2C C-Proα2(I) is best fit as a single homotrimeric species both in the absence of Ca2+ (blue) and in the presence of Ca2+ (red). The best fit is shown as a solid line in the corresponding color. In d–e, the slopes, which vary at each radial position, are directly proportional to the weight average molecular weight for the total protein concentration at that position. d Sedimentation equilibrium data for wild-type C-Proα2(I) in the absence of Ca2+ are best fit as a monomer–dimer equilibrium (primarily monomer; see Supplementary Fig. 4) with an association constant sufficiently small to be approximated as a single species of intermediate weight-average molecular weight, with no evidence of a trimeric species, as shown by the best fit in blue. In the presence of 0.5 mM Ca2+ (red), the data are best fit as a monomer–trimer equilibrium (primarily trimer; see Supplementary Fig. 4). e Sedimentation equilibrium data for C2S C-Proα1(I) in the absence of calcium are best fit as a monomer–dimer equilibrium (primarily monomer; see Supplementary Fig. 5) with an association constant sufficiently small to be approximated as a single species of intermediate weight-average molecular weight, with no evidence of trimeric species, as shown by the best fit in blue. In the presence of 0.5 mM Ca2+ (red), the data are best fit as a monomer–trimer equilibrium (primarily trimer; see Supplementary Fig. 5). Only every third data point is shown (b–e). f Size exclusion chromatography analysis of Asp1277His C-Proα1(I) in the presence and absence of Ca2+, as compared to wild-type C-Proα1(I), reveals the inability of this Ca2+-binding variant to assemble into a homotrimer, despite the presence of both C2 and C3 (left). Immunoblot analysis under non-reducing conditions show the predominant species is a dimer, with other oligomeric products also present (right)