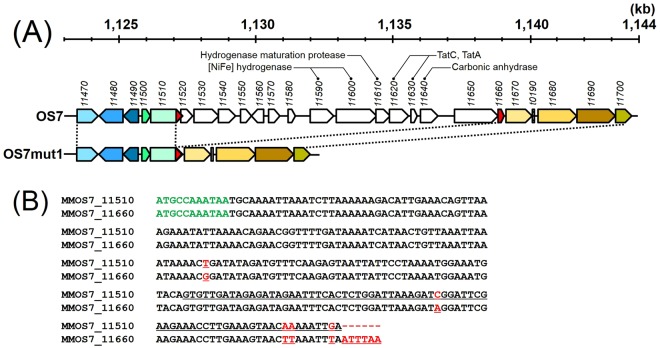
Figure 3.
(A) Genome map of strain OS7 at coordinates 1,123 to 1,144 kb and that of strain OS7mut1 at the corresponding region. Numbers below the genome coordinates indicate locus tags (MMOS7_number). Homologous genes between the two genomes are shown in the same colors. The 3′-end sequence of MMOS7_11510 and the 5′-end sequence of MMOS7_11660 were almost identical; these sequences are shown in red. The gene cluster named “the MIC island” (MMOS7_11520 - MMOS7_11650) is absent in the genome of strain OS7mut1. (B) Alignment of the nucleotide sequence of the 3′-end of MMOS7_11510 and that of MMOS7_11660. The upper sequence shows the 3′-end sequence of MMOS7_11510, the last three bases (TGA) being a stop codon, while the lower sequence shows the MMOS7_11660 sequence, the first three bases (ATG) and the last three bases (TAA) being the initiation and stop codons, respectively. Mismatched sequences are shown in red and underlined. The 3′-end region of the nucleotide sequence of the MMOS7_11510/MMOS7_11660 hybrid gene in strain OS7mut1 was 100% identical to that of MMOS7_11660. The nucleotide sequence of the whole MMOS7_11510/MMOS7_11660 hybrid gene in strain OS7mut1 was 100% identical to the sequences of the corresponding genes in M. maripaludis strains, S2, C5, C6, and C7.