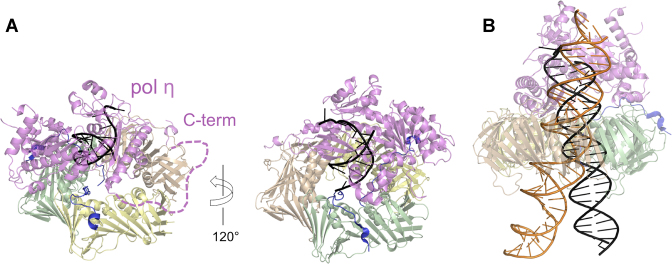
Figure 6.
Structural models of pol η-PCNA holoenzymes with p15 and DNA. (A) The PCNA trimer of the p1550–77–PCNA crystal structure (PDB ID: 4D2G) was superposed to PCNA of the low-resolution structure of human pol η–PCNA–DNA generated from EM data (PDB ID: 3JA9 and 3JAA) (33). DNA is shown in black. The vacant PIP-box site on PCNA (subunit wheat) was occupied by the C-terminal PIP-box of pol η using the crystal structure of human PCNA bound to pol η residues 700–710 (chain W of PDB ID 2ZVK) (40). The dashed line indicates the flexible pol η C-terminus (residues 433–699). (B) The PCNA trimer of the structure of p1550–77–PCNA–DNA complex (PDB: 6EHT) was superposed to PCNA of the pol η–PCNA–DNA (48) complex (PDB: 3JA9 and and 3JAA). The DNA of the first complex (elongated to 40 bp) is shown as an orange ribbon, that of the latter (elongated to 25 bp) as a black ribbon. According to these models, it is possible that p15 may co-exist with pol η on the same PCNA ring. However, the constraint on DNA within the clamp channel imposed by p15 may hinder the translocation of pol η holoenzyme on DNA.