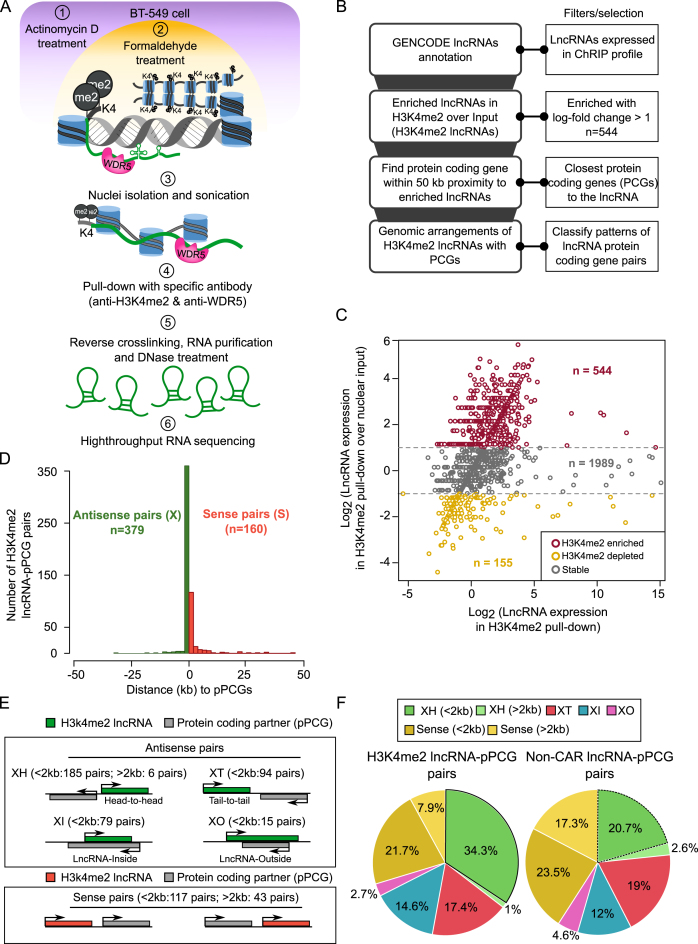
Figure 1.
Characterizing H3K4me2 enriched lncRNAs. (A) ChRIP experimental workflow to identify lncRNAs bound to chromatin enriched with H3K4me2 and WDR5 in BT-549 cell line. (B) Computational approach used for finding chromatin-associated RNAs and enriched patterns of genomic organization with respect to nearest protein coding genes. (C) Scatter plot showing the enrichment of H3K4me2 lncRNAs over input. X-axis denotes log transformed expression values of H3K4me2 lncRNAs and Y-axis denotes log-fold changes of lncRNAs in H3K4me2 ChRIP sample over nuclear input sample. (D) Histogram shows distribution of H3K4me2 lncRNAs with antisense (X) and sense (S) pattern with respect to their protein coding partner (pPCGs). ‘n’ denotes number of lncRNA-pPCG pairs in each pattern. (E) Genomic organization of H3K4me2 lncRNAs (green bars) with respect to nearest protein coding genes (grey bars). XH: where lncRNA shows Head-to-Head arrangement with nearby protein coding gene. XT: lncRNA in Tail-to-Tail arrangement with protein coding gene, XI: lncRNA located inside a protein coding gene, XO: lncRNA located outside and covers the entire protein coding gene. Sense pairs means lncRNAs in the same orientation as protein coding gene. The notion of greater or less than 2 kb means that the partner genes (pPCGs) are located within 2 kb (<2 kb) or away from 2 kb (> 2 kb) but within 50 kb window with respect to H3K4me2 lncRNAs. (F) Distribution of different patterns of genomic arrangements as described in (E) for H3K4me2 lncRNAs and non-CAR lncRNAs.