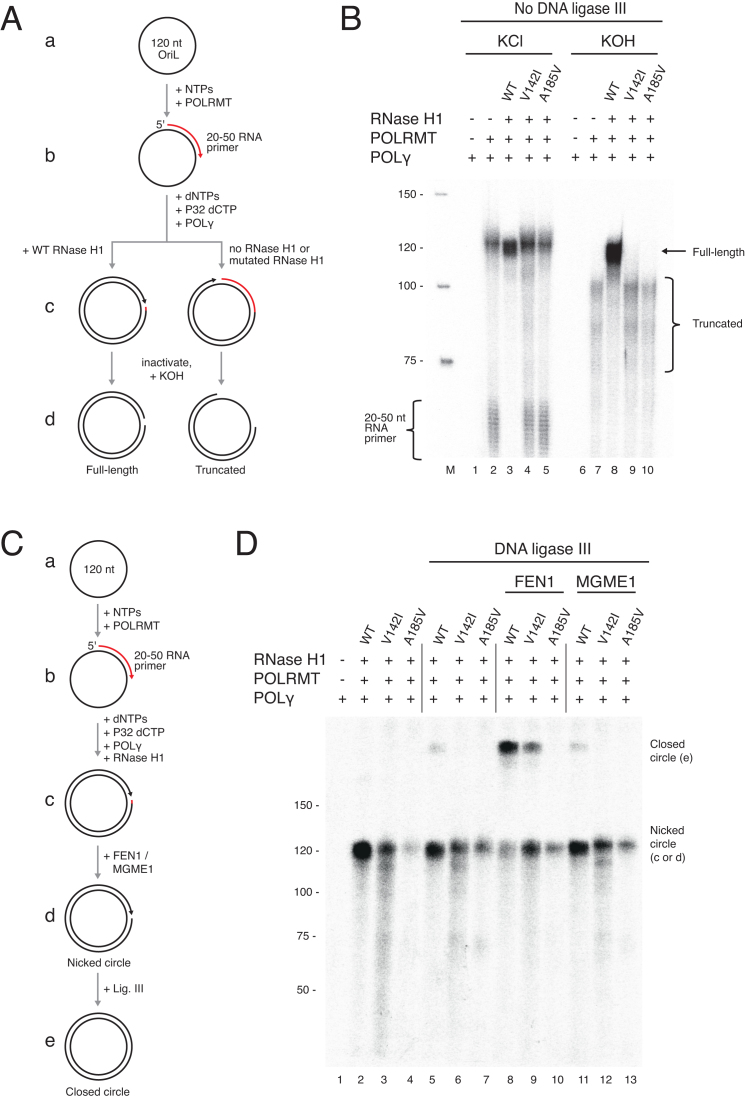
Figure 6.
Reconstitution of primer formation, removal, and ligation of the nascent L-strand. (A) Schematic of the minicircle replication assay in B, using a circular oligonucleotide (120 nt) with OriL-specific sequence. Although shown as consecutive steps, all proteins were added simultaneously. The template was labelled by the incorporation of [α-32P] dCTP during reactions. After inactivation, samples were treated with KOH to hydrolyze RNA. (B) RNase H1 cleaves POLRMT-generated primers after replication is initiated on the minicircle. Lane 1 and lane 6 did not contain POLRMT as a negative control in primer formation, and no labelled product was observed. Short 20–50 nt products represent unutilized primers. After overnight incubation, reactions were stopped and treated with 300 mM KCl as control (lanes 1–5) or KOH (lanes 6–10). Only reactions with wild type RNase H1 were unaffected by KOH treatment (lane 8, full-length band), indicating RNase H1 had processed the POLRMT-delivered primer. Retained RNA due to incomplete primer removal was degraded by KOH, leading to truncated products (lanes 7, 9, 10). It is worth noting that POLRMT seems to be able to incorporate low levels of dCTP, as has previously been shown for T7 RNA polymerase (46), explaining the labeling of the short primers in lanes 2, 4 and 5. (C) Schematic of the minicircle replication assay coupled to ligation used in D. The template was incubated with POLγ, POLRMT, and RNase H1 or mutants and, where indicated, FEN1 or MGME1 for 30 min at 37°C. 300 fmol DNA ligase III was then added (lanes 5–14), and the samples were incubated at 16°C overnight. (D) Efficient ligation (marked closed circle) of minicircle replication products was observed in the presence of FEN1 and wild type RNase H1 (lane 8). Moderate ligation was observed with FEN1 and the V142A RNase H1 mutant (lane 9). MGME1 did not affect ligation efficiency (lanes 11–13). Reactions were performed as shown in C.