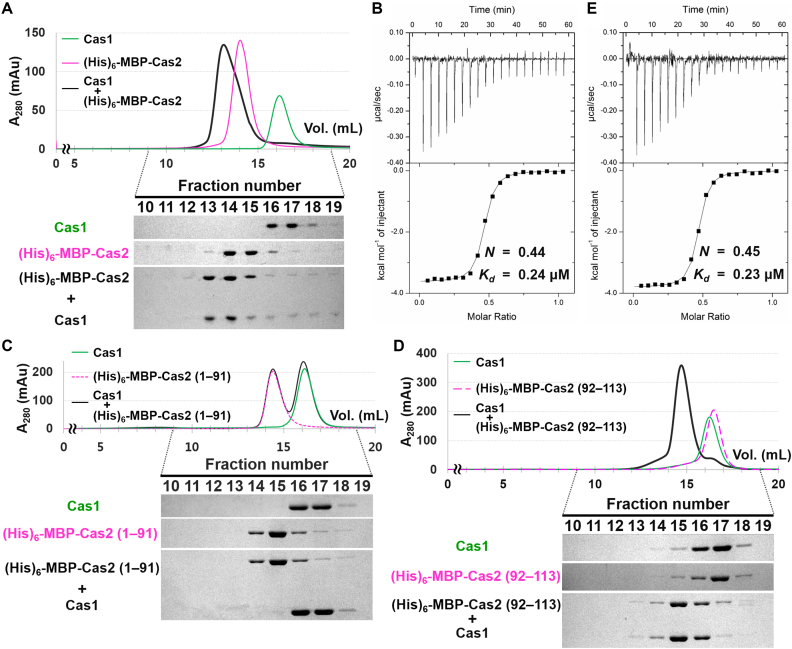
Figure 2.
Cas2 interacts with Cas1 through its C-terminal tail. (A) Interaction between Cas1 and (His)6-MBP-Cas2 determined by analytical SEC. Individually purified Cas1 (20 μM) and (His)6-MBP-Cas2 (20 μM) samples were used. Elution fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Uncropped gel images are shown in Supplementary Figure S18. (B) ITC analysis showing the binding of (His)6-MBP-Cas2 to Cas1. (His)6-MBP-Cas2 (400 μM) was added consecutively to the chamber containing Cas1 (80 μM). The experimentally determined N and Kd values are also indicated. (C and D) The interactions between Cas1 and truncated Cas2 variants were tested in analytical SEC. Cas1 (40 μM) does not interact with the C-terminally truncated form (residues 1–91) of Cas2 (C), but forms a stable complex with the C-terminal tail (residues 92–113) of Cas2 (D). These two Cas2 variants (20 μM) were purified with an N-terminal (His)6-MBP tag. Elution fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Uncropped gel images are shown in Supplementary Figure S18. (E) ITC trace for the binding of the C-terminal tail of Cas2 to Cas1. The peptide corresponding to the C-terminal tail of Cas2 (residues 92–113) was commercially synthesized (BIONICS, Korea). The C-terminal tail of Cas2 (400 μM) was injected into Cas1 (80 μM). The experimentally determined N and Kd values are also indicated.