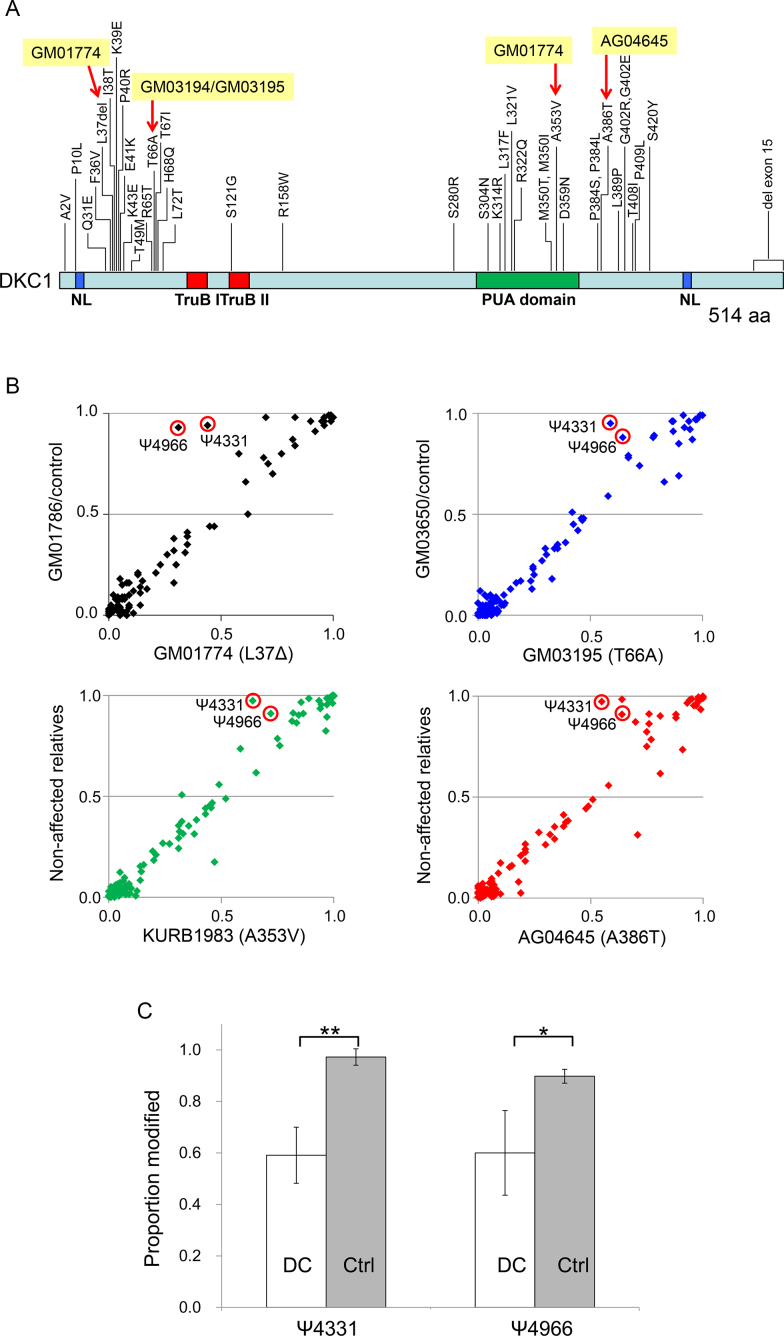
Figure 3.
SILNAS-based PTM analysis of rRNAs from cells derived from DC patients. (A) The positions of amino acid (aa) substitutions or deletions in DKC1 from DC patient cells. The nuclear localization signals (NL) and TruB and PUA domains of DKC1 are indicated. Red arrows denote mutations in patient rRNAs analyzed in this study. The figure was redrawn based on Vulliamy et al. (56) (http://telomerase.asu.edu/diseases.html). (B) Correlation between the stoichiometry of PTM in 28S rRNA from cells of DC patients and healthy controls. The PTMs in all rRNAs from the cells of five DC patients and four non-affected relatives were assessed with SILNAS (Supplementary Tables S3 and S4). The four plots compare the stoichiometry of modification in 28S rRNA derived from four DKC1 mutant cell lines (del37L, A353V, T66A, A386T) vs. control lines, and a significant difference was detected for Ψ4331 and Ψ4966 (red circles). Note that the average stoichiometric value of non-affected relatives was used as the control for Patients KURB1983 and AG4645 because the cells of a relative were not available for Patients KURB1983 and AG4645. (C) Statistical significance of differences in pseudouridylation at positions 4331 and 4966 in 28S rRNA from DC patient cells. Each value represents the mean ± S.D. of five DC patients and four relatives (Ctrl). *P < 0.005, **P < 0.0005 (one-tailed Student's t-test).