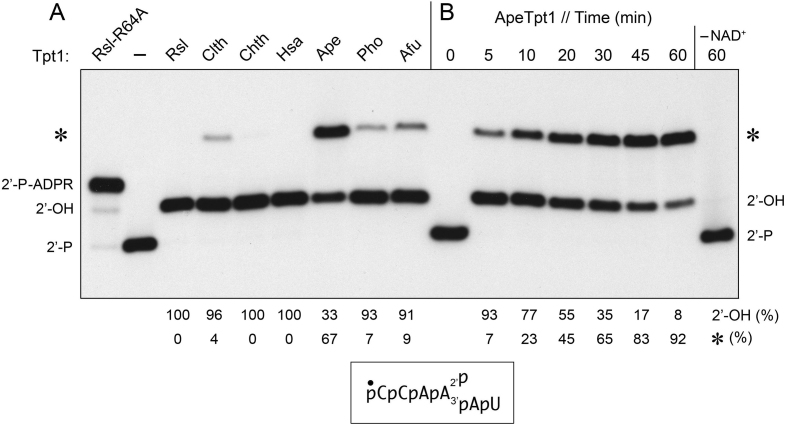
Figure 1.
Formation of a novel RNA product during Tpt1 reaction with 2′-phosphate RNA. (A) Reaction mixtures (10 μl) containing 100 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.5, 0.2 μM (2 pmol) 5′ 32P-labeled 6-mer 2′-PO4 RNA (shown at bottom), 1 mM NAD+, and 0.5 μM (5 pmol) Tpt1 from the sources specified were incubated at 37°C for 30 min. Tpt1 was omitted from the control reaction mixture in lane –. The sources of enzyme are as follows: Runella slithyformis, Rsl; Clostridium thermocellum, Clth; Chaetomium themophilum, Chth; Homo sapiens, Hsa; Aeropyrum pernix, Ape, Pyrococcus horikoshii, Pho; and Archaeoglobus fulgidus, Afu. The step 2-defective RslTpt1-R64A mutant was assayed in parallel (leftmost lane) in order to demarcate the 2′-P-ADPR RNA intermediate in the canonical Tpt1 reaction pathway. The reactions were quenched by adding three volumes of cold 90% formamide, 50 mM EDTA. (B) A reaction mixture containing 100 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.5, 0.2 μM 5′ 32P-labeled 6-mer 2′-PO4 RNA, 1 mM NAD+, and 0.5 μM (5 pmol) ApeTpt1 was incubated at 37°C. Aliquots (10 μl) were withdrawn at the times specified and quenched immediately with three volumes of cold 90% formamide, 50 mM EDTA. The time 0 sample was withdrawn prior to adding ApeTpt1. The reaction products were analyzed by urea-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. The positions of the 6-mer 2′-PO4 RNA substrate (2′-P), 2′-P-ADPR RNA intermediate, and 2′-OH RNA product (2′-OH) of the canonical two-step Tpt1 reaction are indicated on the left and right. The novel RNA product formed by some of the Tpt1 enzymes is denoted by an asterisk. The yields of 2′-OH RNA and novel RNA (expressed as percent of total labeled RNA) are indicated below the lanes.