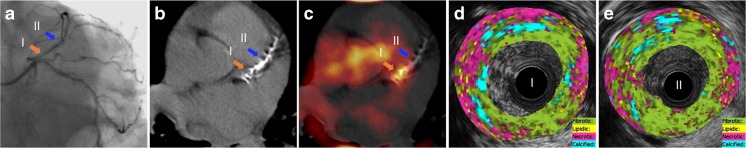
Fig. 3.
Regional coronary uptake of 18F-NaF. A 64-year-old woman with unstable angina. (a), X-ray coronary angiogram of showed severe coronary stenosis at proximal (I) and mid (II) segments of LAD; Cardiac CT (b) and 18F-NaF PET/CT (c) showed regional distribution of 18F-NaF uptake within an atheromatous lesion. Representative LAD lesions showed distinct tracer accumulation along a severely fibrocalcific lesion. Prominent focal 18F-NaF uptake were observed at coronary segment I verse absent focal uptake at segment II. Anatomical IVUS indicate the presence of fibroatheromatous lesion with prominently increased necrotic (35% vs. 23%) and calcified tissue (10% vs. 6%) also a slightly higher proportion of lipidic tissue (9% vs.8%), but decreased fibrotic tissue (46 vs 62%) in segment I (d) in comparison to segment II (e)