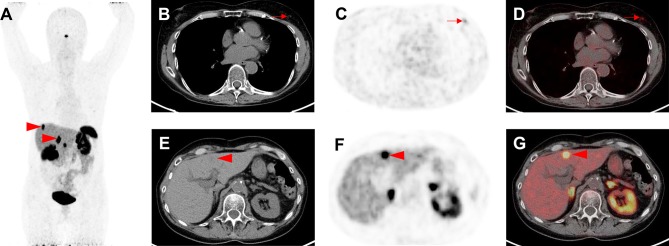
Fig. 5.
Indeterminate findings on somatostatin receptor (SSTR) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT). A 63-year-old man with history of a gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, who underwent [68Ga]-labeled 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-N,N′,N′′,N′′′-tetraacetic acid-d-Phe(1)-Tyr(3)-octreotide ([68Ga]-DOTATOC) PET/CT for staging. a Whole-body maximum intensity projection image demonstrates suspicious radiotracer uptake (red arrowheads) in the liver. b Axial CT, c axial PET and d axial PET/CT show mild radiotracer uptake in the left breast (red arrows). This has been classified as SSTR-RADS-3C by an experienced reader. e Axial CT, f axial PET, and g axial PET/CT demonstrate intense radiotracer uptake in multiple liver lesions (one of which is demarcated by the red arrows). As there is subtle hypoattenuation in the liver on e axial CT, this finding was classified as SSTR-RADS-5 and, therefore, the overall SSTR-RADS score was 5. Based on this scoring, peptide receptor radionuclide therapy should be considered [20]