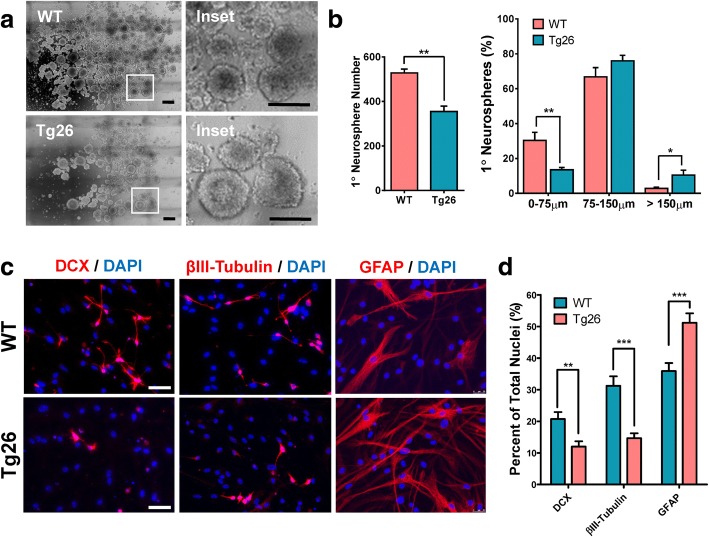
Fig. 2.
In vitro stemness and neural lineage differentiation are impaired in HIV-1 Tg26 transgenic mice. a, b Fewer number of primary neurospheres but higher proportion of larger sized neurospheres in Tg26 mice. Representative tiled images of SVZ-derived primary neurospheres at 7 days in vitro are shown (a), and the number of the size stratified primary neurospheres was quantified using ImageJ software (b). Data is presented as the mean ± SEM from four mice per genotype. c, d Reduced neuronal lineage differentiation but increased astroglial lineage differentiation in Tg26 mouse NSCs/NPCs. Dissociated NSCs/NPCs from primary neurospheres were differentiated for 5 days followed by immunocytochemistry with cell lineage-specific antibodies to assess for neuroblast (DCX) and neuronal (β3 tubulin) differentiation, and astrocytic (GFAP) formation (c). Tg26 mouse NSCs were unable to form as many neuroblasts or neurons as wild-type (WT) mouse NSCs, but instead formed more astrocytes (d). The quantitative differentiation data is presented as the Mean ± SEM from 4 mice (2 males and 2 females per genotype), with five to eight random fields per mouse for each cellular marker. Scale bar in a, 300 μm; inset, 150 μm. Scale bar in c 50 μm. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001