Figure 2.
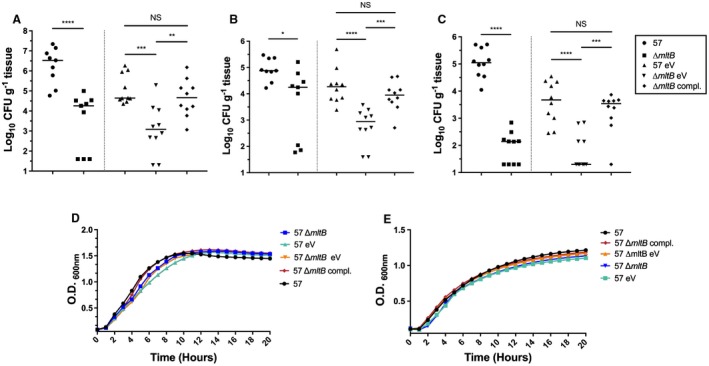
Colonization of the bloodstream by the mltB mutant. Colonization of the spleen (A), liver (B) and kidneys (C) was determined by infecting CBA/J mice with 107 CFU of either the WT strain (57) or its derivative strains. At 24 hpi, mice were sacrificed, organs were harvested, and the bacterial burden was determined by CFU enumeration on LB agar (57 and ∆mltB) and LB‐Km agar (57 eV, 57 ∆mltB eV and 57 ∆mltB compl.). Bacterial numbers are presented as the log10 CFU g–1 of tissue. Each data point represents a sample from an individual mouse, and horizontal bars indicate the median values. Statistical significance was calculated by the Mann‐Whitney test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.0005; ****p < 0.0001; NS, not significant). D and E. Growth of the WT (57) and its derivative strains. (D) LB. (E) M9 minimal medium supplemented with 0.4% Glucose and 0.2% casamino acids. Results from in vitro experiments are the mean values and standard deviations of three biological experiments. For ease of reading, standard deviations were removed from graphs D and E. Abbreviation: 57: WT (AB0057Km); eV: empty vector (pABBR_Km); compl.: complemented (pABBR_Km‐mrdB‐mltB).
