Figure 2. Accessory editing components of the RECC enzyme.
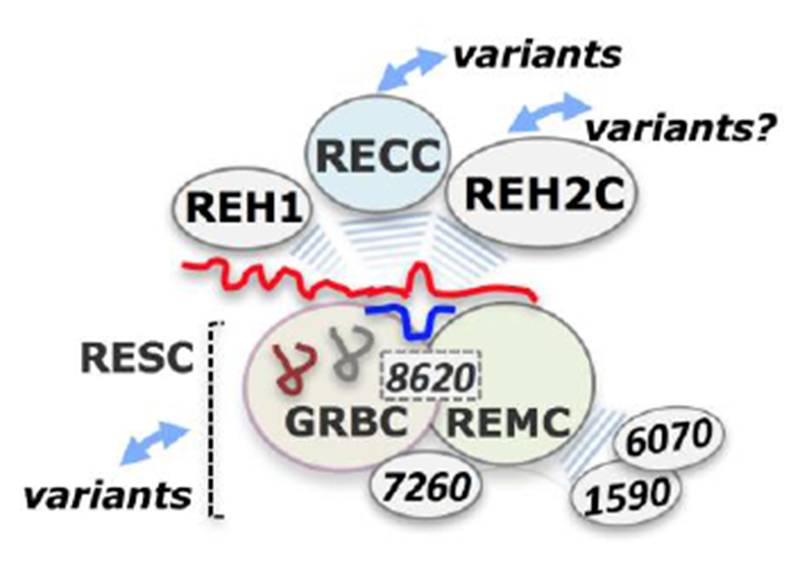
Core and accessory components of the editing apparatus assemble around the mRNA substrates. These include the gRNA-bound RESC subcomplex, the REH2C helicase subcomplex, a MRB1590/6070-containing subcomplex, and REH1 helicase. The core RECC enzyme and its accessory editing factors have been found to associate with each other via transient RNA-mediated interactions. RESC is divided into two functionally distinct modules, the GRBC and REMC. Several RESC proteins may be critical for the integrity and organization of RESC. MRB8620, a canonical GRBC protein, may control the assembly of the GRBC/REMC modules in RESC (MRB8620 is depicted as a dotted box bridging the two modules). MRB7260 binds weakly with RESC proteins and is not a canonical protein. It may be an assembly factor of RESC. Purifications of RESC and REH2C proteins were shown to contain mRNA substrates and products of editing. This supports a current model of the RNA editing machinery in which RESC-mediated targeting of mRNA or its mRNPs creates suitable mRNA-gRNA hybrid substrates for the RECC and RNA helicase enzymes and other factors during concerted phases of editing: substrate recognition, editing initiation and progression, complex organization and co-complex dynamics. Identified variants of RECC, RESC and potentially other mRNA trans factors may provide additional layers of complexity and control points in editing.
