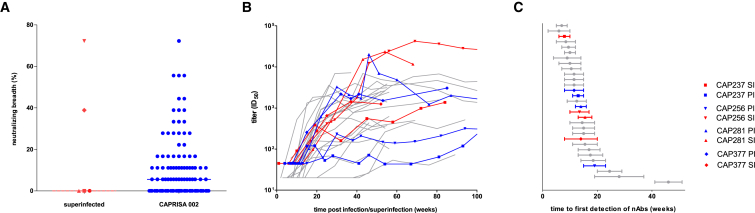
Figure 1.
Potent Neutralizing Antibody Responses Arose to Superinfecting Viruses with a Similar Time to Detection as Primary HIV Responses
(A) Comparison of neutralization breadth (percentage of heterologous viruses neutralized) present in plasma sampled 2 years post-infection between superinfected participants (n = 5) and remaining CAP002 cohort participants (n = 119). Antibody breadth was compared at 2 years post-infection as all superinfected participants had at least 2 years of antiretroviral-naive follow-up. Furthermore, if cross-neutralizing antibodies do not develop by 2–3 years post-infection, they are unlikely to do so subsequently (Gray et al., 2011, Landais et al., 2016, Mikell et al., 2011). Cross-neutralization data at 2 years were available for 120 anti-retroviral-therapy-naive participants.
(B) Autologous neutralizing antibody titers, over time, to superinfecting Envs (red), primary infecting Envs in participants later superinfected (blue), and to early/founder Envs from other CAPRISA participants (gray) (n = 22).
(C) Estimated time, in weeks, from transmission until the first detection of these neutralizing antibody responses. The error bars represent the range given the 95% confidence interval for the timing of superinfection.