Fig. 3.
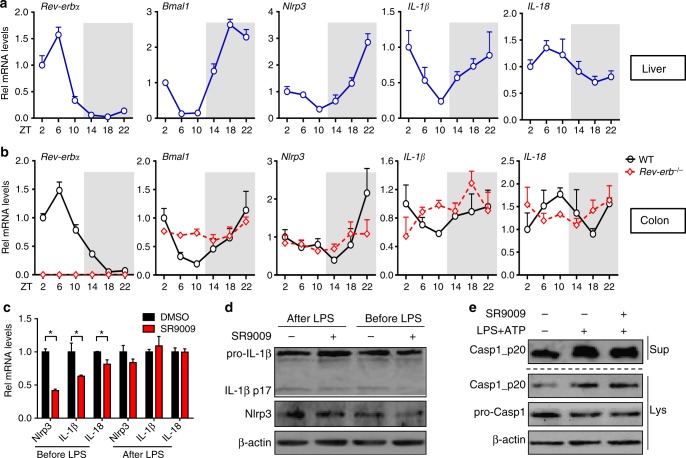
Identification of Nlrp3 as a clock-controlled gene. a qPCR assays on circadian gene expressions of lives from WT mice. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5). b qPCR assays on circadian expressions of colons from WT and Rev-erbα−/− mice. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5). c qPCR measurements of Nlrp3 and related genes in PMs after co-treatment of SR9009 (for 8 h) and LPS. LPS was added before or after SR9009 treatment. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05 (Mann–Whitney U test). d Western blotting of PMs after co-treatment of SR9009 (for 12 h) and LPS/ATP. LPS was added before or after SR9009 treatment for 3 h, followed by ATP addition for 30 min (added last). e Western blotting of PMs after treatment of SR9009 and LPS/ATP. PMs were pretreated with SR9009 or vehicle for 1 h, and then stimulated with LPS/ATP for 0.5 h. Each western blot is representative of three independent experiments (statistical differences between blot density levels were analyzed by Mann–Whitney U test, Supplementary Figure 12). The concentrations of SR9009, LPS, and ATP for cell treatment were 10 μM, 100 ng/ml, and 2 mM, respectively