Fig. 6.
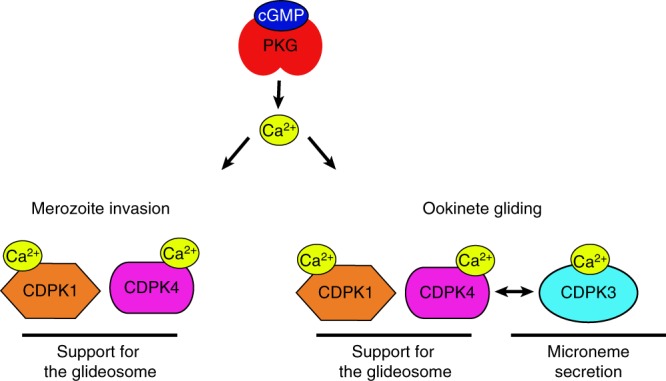
Schematic representation of the CDPK networks downstream of PKG-mediated calcium signals. PKG acts as a stage-transcending calcium regulator that activates multiple CDPKs with stage-specific functions. In merozoites, calcium activates both CDPK4 and 1 to support the activity of the acto-myosin motor. In ookinetes, PKG-dependent calcium signals are required for efficient gliding through CDPK4 and 1 activation and microneme secretion via CDPK3 regulation. Under physiological activation of PKG, CDPK1 and CDPK4 may functionally complement each other to sustain the acto-myosin motor function, while hyperactivation of PKG by chemical or genetic inhibition of phosphodiesterase or adaptation to gene deletion may allow further complementation by CDPK3 in ookinetes24. Note that other kinases such as CDPK5 or the protein kinase A (PKA) are possibly part of this network but the exact links with PKG and these kinases could not be revealed by this study and remain unmapped
