Fig. 5.2.
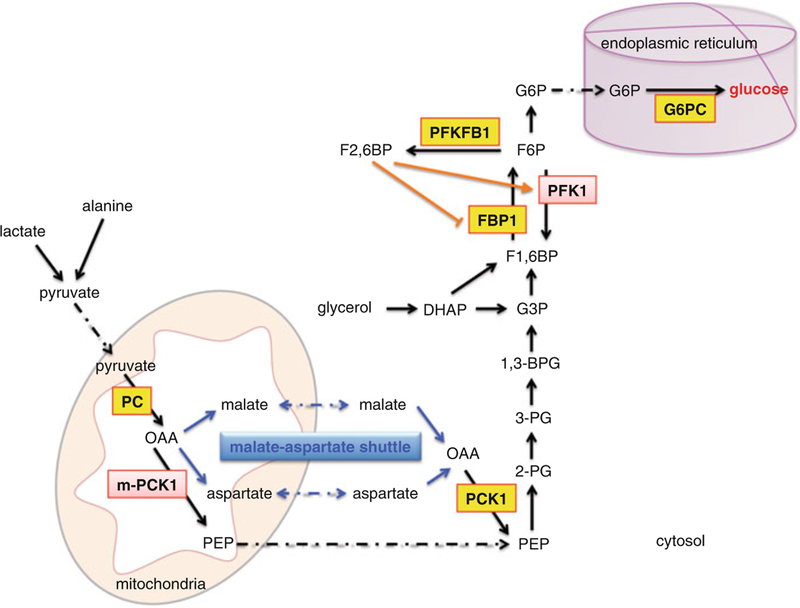
Gluconeogenic pathway in hepatocytes. Lactate and alanine are converted to pyruvate, which enters the mitochondria and is then converted to OAA by enzyme PC. Through malate-aspartate shuttle, OAA exits the mitochondria to form PEP. OAA can also be converted to PEP directly within the mitochondria. PEP then feeds into the gluconeogenic pathway. In addition, glycerol is metabolized to DHAP, which is then converted directly or indirectly through G3P to F1,6BP. The final product, glucose, is produced in the ER by enzyme G6PC. The key enzymes are boxed, with GR primary targets shown in yellow. Abbreviation: OAA oxaloacetate, PEP phospho-enolpyruvate, DHAP dihydroxyacetone phosphate, G3P glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, F1,6BP fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, 2-PG 2-phosphoglycerate, 3-PG 3-phosphoglycerate, 1,3-BPG 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, G3P glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, F1,6BP fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, F2,6BP fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, F6P fructose-6-phosphate, and G6P glucose-6-phosphate. Enzyme abbreviation: PC pyruvate carboxylase, m-PCK1 mitochondrial phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, PCK1 cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, FBP1 fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1, PFK1 phosphofructokinase 1, PFKFB1 phosphofructokinase 2/fructose bispho-sphatase 2, G6PC glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit
