Fig. 2.
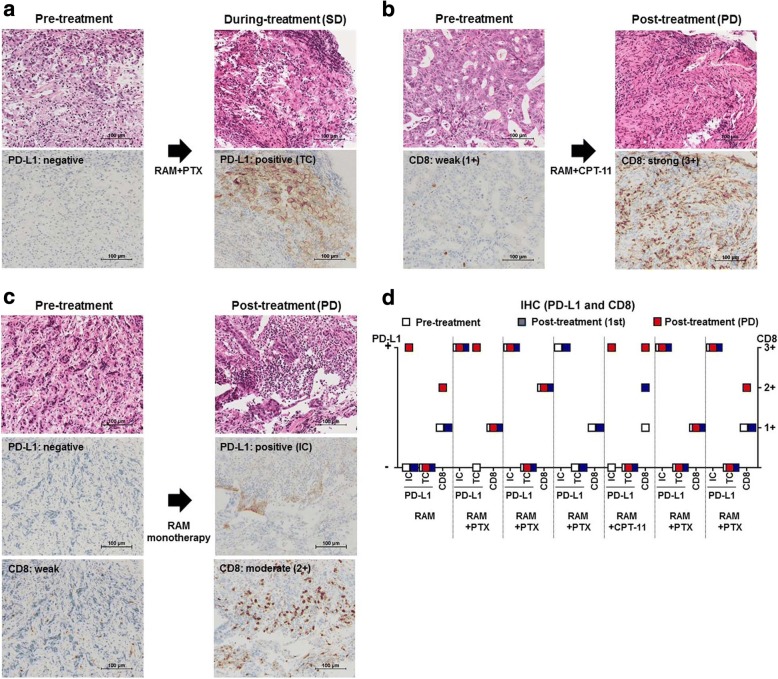
PD-L1 expression and CD8+ T-cell infiltration by IHC. a Hematoxylin–eosin (HE) staining and IHC for PD-L1 in a 67-year-old male with advanced GC. The pre-treatment sample was negative for PD-L1 in both tumor cells and immune cells. After 4 weeks of RAM and PTX treatment, the patient attained SD, and tumor cells were positive for PD-L1. b HE staining and IHC for CD8 in a 79-year-old female with advanced GC. At pre-treatment, CD8 staining was weak (1+). After 10 weeks of RAM and CPT-11 treatment, the patient experienced PD, and CD8 staining was strong (3+). c HE staining and IHC for PD-L1 and CD8 in a 73-year-old female with advanced GC. The pre-treatment sample was negative for PD-L1 in both tumor cells and immune cells, while CD8 staining was weak (1+). After 23 weeks of RAM monotherapy, the patient experienced PD. Immune cells in the post-treatment sample were PD-L1-positive; CD8 staining was moderate (2+). d Summary of IHC. The PD-L1 status in tumor and immune cells changed to positive in 3 of 7 patients post-treatment [1, tumor cells positive (1/7); 2, immune cells positive (7/7). CD8+ T-cell infiltration was weak (1+) in 6 patients and moderate (2+) in 1 patient prior to the initiation of therapy. CD8+ T-cell infiltration was increased in 3 patients. Both PD-L1 expression and CD8+ T-cell infiltration increased after treatment in 2 patients. TC, tumor cells; IC. immune cells