Figure 2.
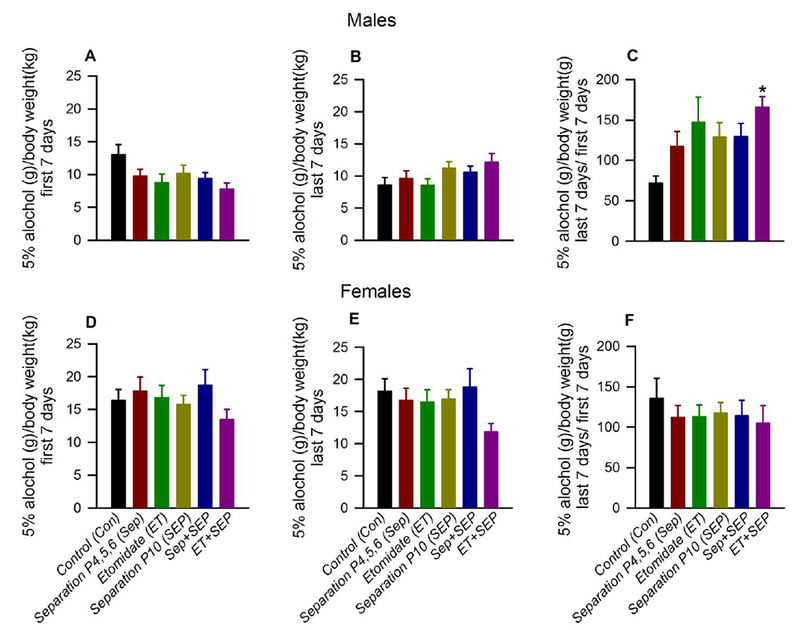
Anesthesia with etomidate (ET) for 2 h at postnatal days (P) 4, 5 or 6 followed by maternal separation for 3 h at P10 led to an increase in 5% ethanol intake in male, but not female, adult rats. Shown are: (A) mean daily 5% ethanol intake first 7 days [ethanol intake (grams) on each day was normalized to body weight (kilograms) then averaged for each animal]; (B) mean daily intake last 7 days; and (C) the intake ratio (mean daily intake last 7 days / mean daily intake first 7 days, in g ethanol / kg body weight) for male rats. (D-F) show respective data for female rats: (D) mean daily intake first 7 days; (E) mean daily intake last 7 days; and (F) the intake ratio. Data are means ± SEM from 13-16 rats per experimental group. *P < 0.05 vs. the Con group. Color coding in Fig. 2D-F is applicable to the entire figure.
