Fig. 3.
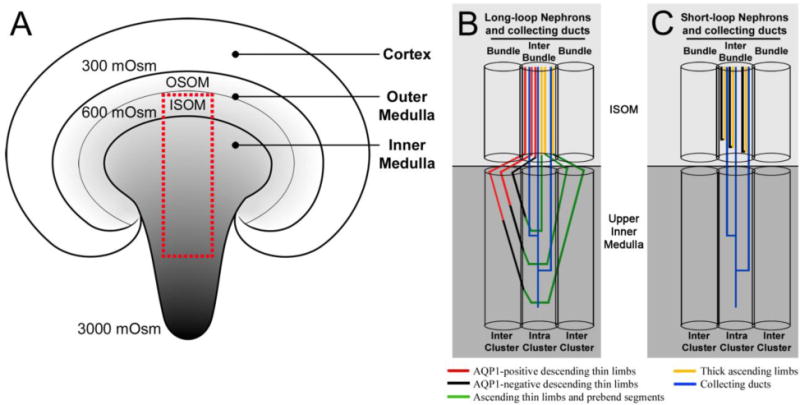
Diagrammatic coronal section of the rodent kidney and medullary nephron and collecting duct architecture. A: The corticomedullary osmotic gradient increases from the cortex to the tip of the inner medulla (reaching a maximum of 3000 mOsmol kg−1 H20 in the rat). OSOM, outer stripe of the outer medulla; ISOM, inner stripe of the outer medulla. The red box represents the area occupied by nephrons and collecting ducts shown in B and C. The medullary architecture of long-loop nephrons (B) and short-loop nephrons (C) is depicted in schematic diagrams alongside collecting duct (CD) clusters. The ISOM consists of two lateral regions (bundle and interbundle) and the upper inner medulla consists of two lateral regions (intercluster and intracluster). Modified from Wei et al. 2015, with permission.
