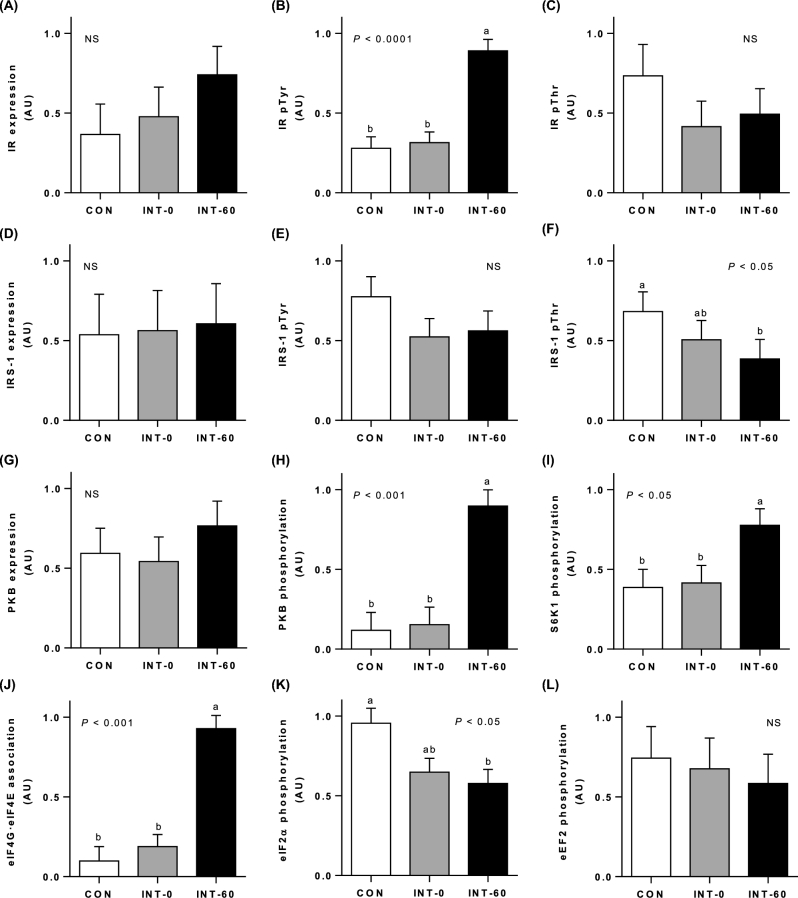
FIGURE 4.
Insulin pathway and translation initiation signaling. IR expression (A), IR pTyr (B), IR pThr (C), IRS-1 expression (D), IRS-1 pTyr (E), IRS-1 pThr (F), PKB expression (G), PKB phosphorylation (H), S6K1 phosphorylation (I), association of the eIF4G–eIF4E complex (J), eIF2α phosphorylation (K), and eEF2 phosphorylation (L) in the longissimus dorsi muscle of neonatal pigs fed for 21 d either continuously or intermittently with measurements made just before (INT-0) or 60 min after (INT-60) a meal. Values are means ± SEMs; n = 6. Statistical analyses were conducted by using mixed-model ANOVA. When a significant effect was detected, all means were compared using a Tukey-Kramer post hoc test. “NS” denotes no significant differences between treatments. Means without a common letter differ significantly. AU, arbitrary units; CON, continuously fed; eEF2, eukaryotic elongation factor 2; eIF, eukaryotic initiation factor; INT, intermittently fed; IR, insulin receptor; IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate 1; PKB, protein kinase B; pThr, threonine phosphorylation; pTyr, tyrosine phosphorylation; S6K1, ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1.