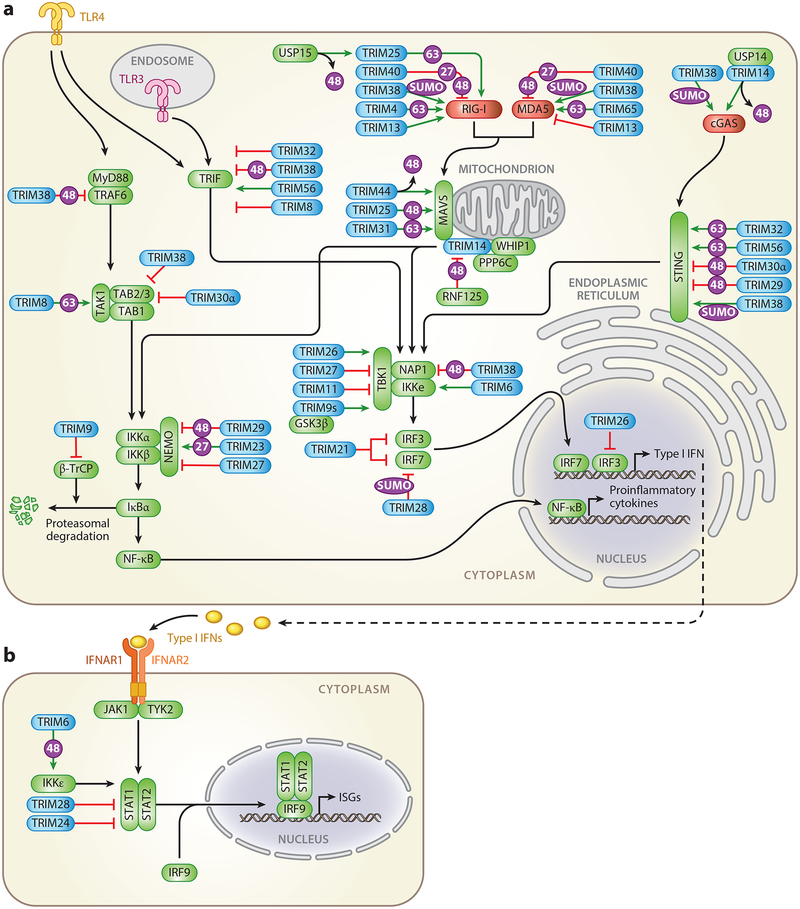
Figure 2.
TRIM-mediated regulation of innate immune signaling pathways. Overview of the TRIM proteins (blue) that positively (green arrows) or negatively (red lines) regulate (a) PRR-mediated induction of type I IFNs and proinflammatory cytokines or (b) IFNAR-induced expression of ISGs. Intracellular receptors are illustrated in red. Signaling intermediates or transcription factors are illustrated in green. Abbreviations: cGAS, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; 27, K27-linked polyubiquitination; 48, K48-linked polyubiquitination; 63, K63-linked polyubiquitination; IFN, interferon; IFNAR, IFNα/β receptor; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; ISG, interferon-stimulated gene; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein; MDA5, melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; PRR, pattern-recognition receptor; RIG-I, retinoic acid-inducible gene-I; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; SUMO, SUMOylation; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TRIM, tripartite motif protein; USP, ubiquitin-specific peptidase, WHIP, Werner helicase interacting protein 1.