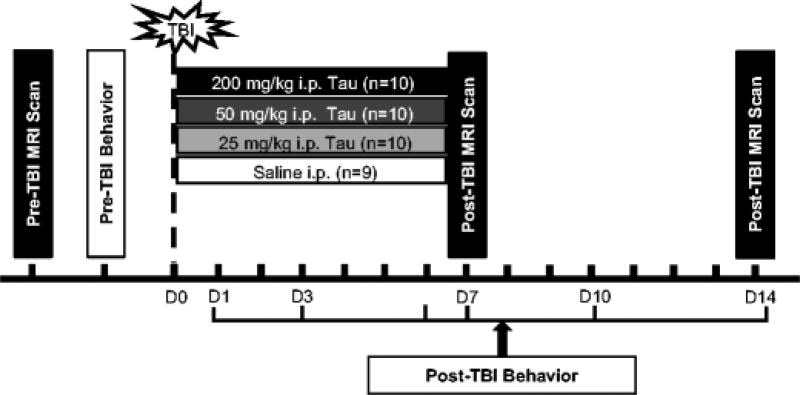
Fig. 1.
Schematic of study design. Baseline magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed on 20–22 month old male F344 rats prior to receiving a traumatic brain injury (TBI). Rats were trained on behavioral tasks for 5 days immediately prior to the day of injury. TBI was induced by controlled cortical impact and animals were randomized into four treatment groups (saline and 25 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg, or 200 mg/kg taurine). Behavioral tests of sensorimotor function were performed on post-TBI day 1, 3, 7, 10 and 14 for each group. MRI was performed on post-injury day 14 to quantify brain tissue loss.