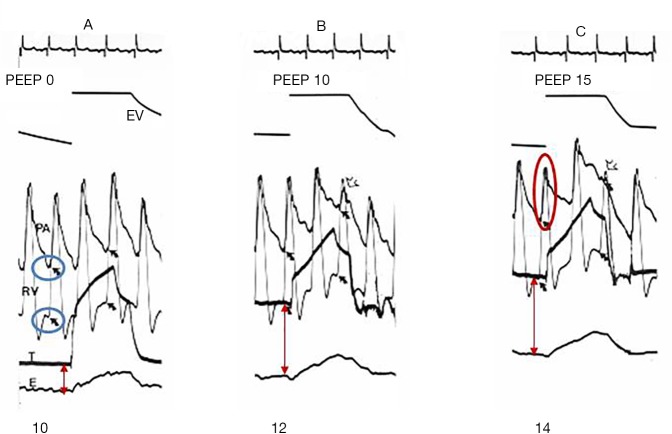
Figure 5.
Evaluation of a PEEP trial effect in ARDS using Pes. The left panel (A) represents the PA, RV and esophageal pressures recorded in ZEEP conditions. PTP (red arrow) is low and the RV isovolumetric pressure (between the 2 black arrows), which reflects RV afterload, is 10 cmH2O. In 10 (B) and 15 (C) cmH2O PEEP, PTP increases significantly at end-expiration and is responsible for an increase in RV afterload, attested by an increase in RV isovolumetric pressure to 12 and 14 cmH2O, respectively. Note that the PA pulse pressure (red circle), which reflects the RV stroke volume, decreases with the increase in RV afterload. Blue circles represent closing of the tricuspid valve and opening of the pulmonary valve with the beginning of RV ejection. PEEP, positive end-expiratory pressure; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; PA, pulmonary artery; PTP, transpulmonary pressure; RV, right ventricle.