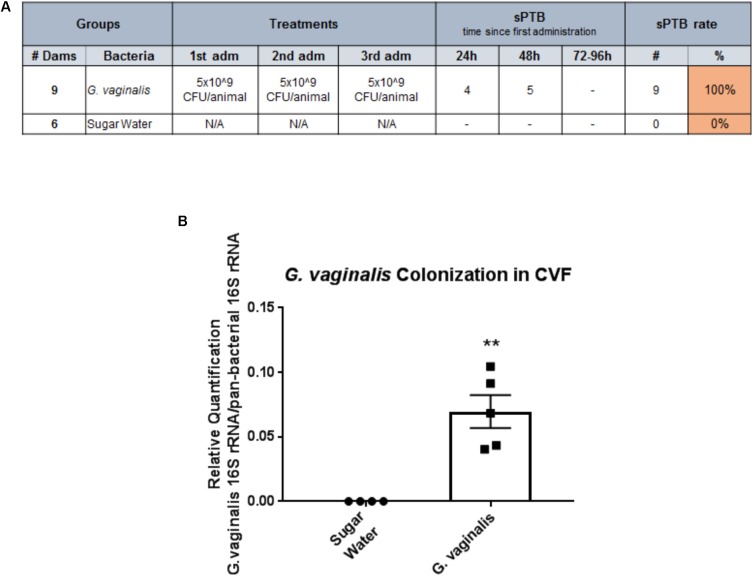
FIGURE 7.
Intravaginal inoculation of G. vaginalis results in PTB and colonization of the cervicovaginal space. (A) G. vaginalis (5 × 109 CFU/animal) was inoculated intravaginally into timed pregnant C57/B6 mice on embryonic day E13, E14, and E15. Sugar water inoculated animals acted as controls. Animals were observed for PTB daily until term. Table shows the dose of G. vaginalis inoculation at each administration, the number of dams delivering preterm on each day following the first inoculation, and the PTB percentage. (B). G. vaginalis (5 × 109 CFU/animal) was inoculated intravaginally into timed pregnant C57/B6 mice on E13. Animals were sacrificed 24 h after inoculation. Cervicovaginal fluid (CVF) was collected for gDNA isolation and measurement of the 16S gene of G. vaginalis by QPCR. Sugar water inoculated animals acted as controls. Values are mean ± SEM. ∗∗p < 0.01.