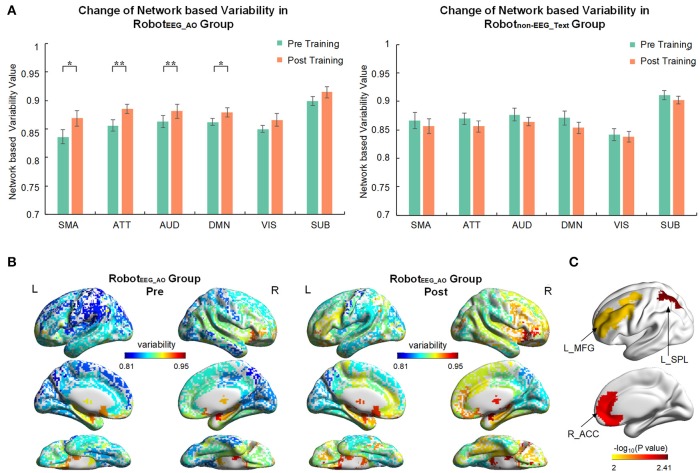
Figure 4.
Brain network variability changes after the interventions. (A) Comparison of variability in six brain subnetworks between pre and post training in two groups. Only four out of six subnetworks had significant change after training in RobotEEG_AO group while no significant change in any subnetwork in Robotnon−EEG_Text group. Error bars are standard errors. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. SMA, sensory-motor areas; ATT, attention network; AUD, auditory network; DMN, default mode network; VIS, visual recognition network; SUB, subcortical network. (B) Whole-brain variability topography before and after training for RobotEEG_AO group. Higher variability indicates a more flexible role of one region that may participate in multiple functions. The variability has been averaged across all the subjects in the group. (C) Brain regions showing significant increase in variability after the intervention based on the paired t-test (P < 0.01) for the RobotEEG_AO group. L_MFG, left middle frontal gyrus; L_SPL, left superior parietal lobule; R_ACC, right anterior cingulate cortex.