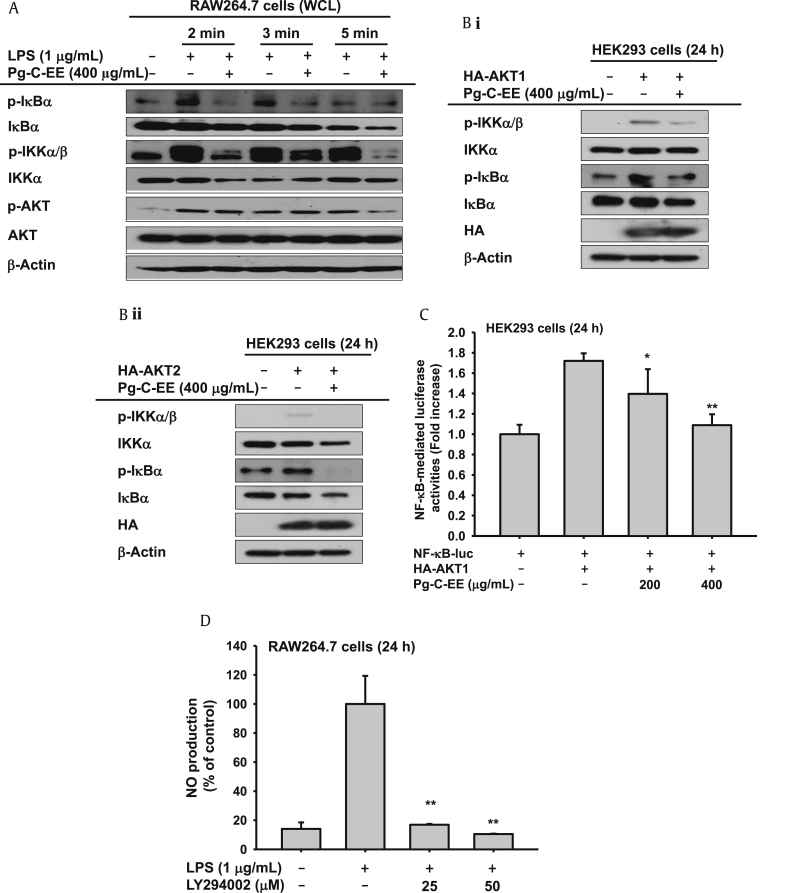
Fig. 3.
Effect of Pg-C-EE and LPS on the activation of upstream signaling protein for the NF-κB pathway. (A) RAW264.7 cells were incubated with LPS (1 μg/mL) in the presence or absence of Pg-C-EE. After preparing WCLs, the expression of total or phosphorylated IκBα, IKKα/β, IKKα, and AKT was identified using immunoblotting analysis. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with AKT1 (i) and AKT2 (ii) for 24 h and were then treated with Pg-C-EE for an additional 24 h. After preparing WCLs, expression of total or phosphorylated IκBα, IKKα/β, and AKT as well HA, a tagging protein of AKT1 and AKT2, was detected by immunoblotting analysis. (C) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with NF-κB-Luc and AKT1 as well as β-Gal plasmid constructs in the presence or absence of Pg-C-EE. (D) Level of NO production released from LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells treated with LPS in the presence or absence of LY294002 was measured by Griess assay. AKT, protein kinase B; β-Gal, β-galactosidase; HA, hemagglutinin; IKK, inhibitor of κB kinase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; Pg-C-EE, ethanolic extract of Panax ginseng berry calyx; WCL, whole cell lysates.