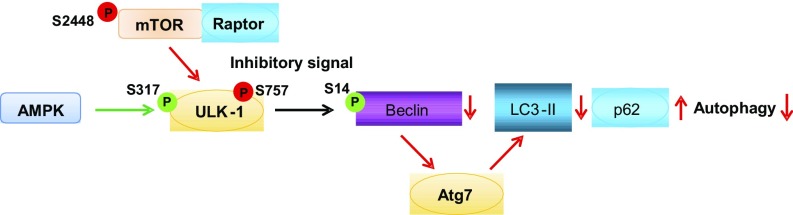
Fig. 1.
Schematic of mTOR and autophagy signaling. Upon activation, mTOR phosphorylates ULK-1 at S757, a target of mTORC1 and a well-established antiautophagy site. This, in turn, sequesters ULK-1 away from AMPK, which phosphorylates and activates ULK-1 at S317. Phosphorylation of ULK-1 at S317 promotes phosphorylation and activation of Beclin-1 at S14, a critical step in the nucleation phase of autophagy. Beclin-1 promotes lipidation of LC3-I to generate its lipidated form LC3-II, enabling elongation of the limiting membrane and formation of autophagosomes. Lipidation of LC3-I is an ubiquitin-like reaction that requires Atg7. Autophagosomes act via protein adaptors such as p62 to deliver proteins and organelles to lysosomes for degradation.