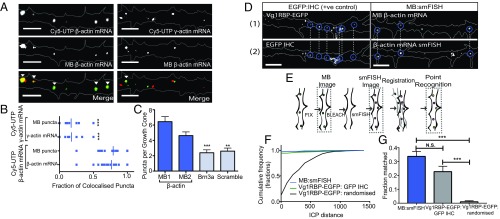
Fig. 2.
Molecular beacons label β-actin mRNA in growing axons. (A) MBs colocalize significantly more with exogenous fluorescently tagged β-actin mRNA than with exogenous fluorescently tagged γ-actin mRNA in growing RGC axons. (Scale bars: 5 μm.) (B) Quantification of colocalization between β-actin mRNA-targeting MBs and exogenous Cy5-UTP β-actin mRNA and Cy5-UTP γ-actin mRNA. P < 0.0001, n = 21 axons and 11 axons, respectively. (C) MBs targeting β-actin mRNA showed significantly more puncta per growth cone than control MBs targeting Brn3a mRNA or a scrambled sequence. **P = 0.0043, ***P = 0.001, unpaired t test. n = 64, 73, 82, and 86 axons for β-actin MB1, β-actin MB2, Brn3a, and the scrambled sequence, respectively. (D) MBs and smFISH puncta could be observed to mark the same place in nonsimultaneous images, similar to EGFP puncta and IHC against EGFP. (Scale bars: 5 μm.) (E) Schematic showing the workflow for the registration of nonsimultaneous images used to quantify colocalization. (F) Cumulative frequency distribution of ICP distance between matched puncta in MB and smFISH images (n = 14 axons) and in Vg1RBP-EGFP and IHC positive and randomized negative controls (n = 11 axons). (G) Quantification of colocalization based on an ICP distance threshold of 1. ***P < 0.0001, unpaired t test; N.S., not significant.