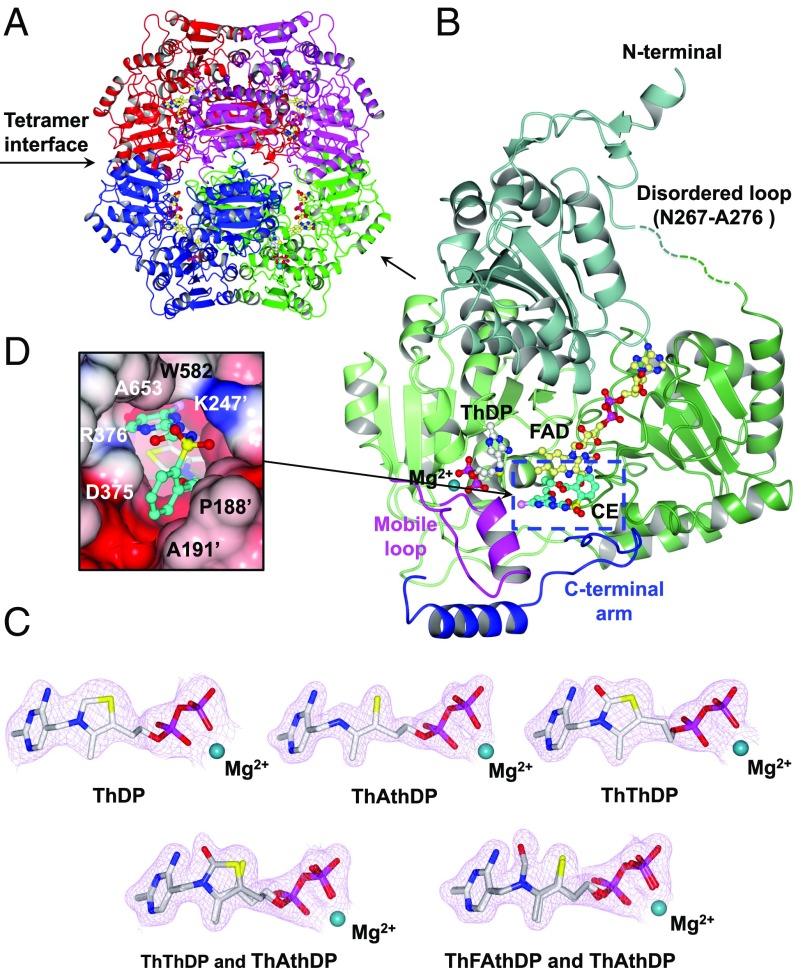
Fig. 2.
CaAHAS structure. (A) Overall fold of the uninhibited CaAHAS tetramer in cartoon representation. The cofactors ThDP (white) and FAD (yellow) are drawn as ball and sticks models, and the magnesium ion is depicted as a dark cyan sphere. (B) Cartoon representation of a single subunit of CaAHAS in complex with CE. The three domains: α (76–272), β (273–454), and γ (468–639) are colored in different shades of green. The two elements of the capping region, the “mobile loop” (Q576-Y591) and “C-terminal arm” (P646-Y683), which are key for trapping the herbicide in its binding pocket, are colored magenta and blue, respectively. The carbon atoms in CE are colored cyan. A green broken line represents the N267–A276 region, which is disordered in all structures. (C) 2Fo − Fc electron density maps (contoured at ≥2.0 σ) for ThDP, ThAthDP, ThThDP, ThThDP/ThAthDP, and ThFAthDP/ThAthDP in the uninhibited enzyme (2.9-Å resolution), the IE (1.8-Å resolution), PC (2.4-Å resolution), MT (2.1-Å resolution), and CE (2.1-Å resolution) complexes, respectively. (D) Connolly surface showing CE (cyan) inserted into the substrate access channel thereby blocking the active site, where ThDP (white) is located (enclosed in B with broken lines). Nitrogen, blue; oxygen, red; sulfur, yellow; potassium, magenta; and chlorine, pink.