Fig. 4.
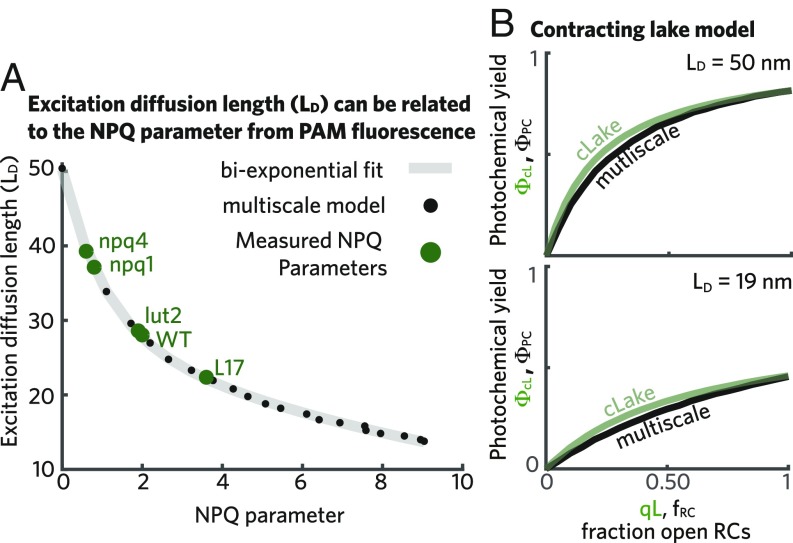
Interpreting PAM Chl fluorescence in the presence of a variable excitation diffusion length. (A) The excitation diffusion length is plotted as a function of the NPQ parameter extracted from Chl fluorescence simulations (black dots). A biexponential fit to these data given by is shown as a gray line. The green dots indicate the measured steady-state values of the NPQ parameter of several qE mutants at 1,200 mol photons : L17, a PsbS overexpressor (8), as well as npq1, lut2, and npq4, which are lacking Zea, lutein, and PsbS, respectively (42). The wild-type measurement is also taken from ref. 42. (B) The photochemical yield as a function of the fraction of open RCs is plotted for both the contracting lake model (cLake; green line) and the multiscale model (black line) when nm (Upper) and when nm (Lower). For the case of the cLake, the x axis corresponds to the qL parameter extracted from PAM measurements.