Figure 6. Schematic structure of AKAP5 and its complexes with AMPARs and Cav1.2.
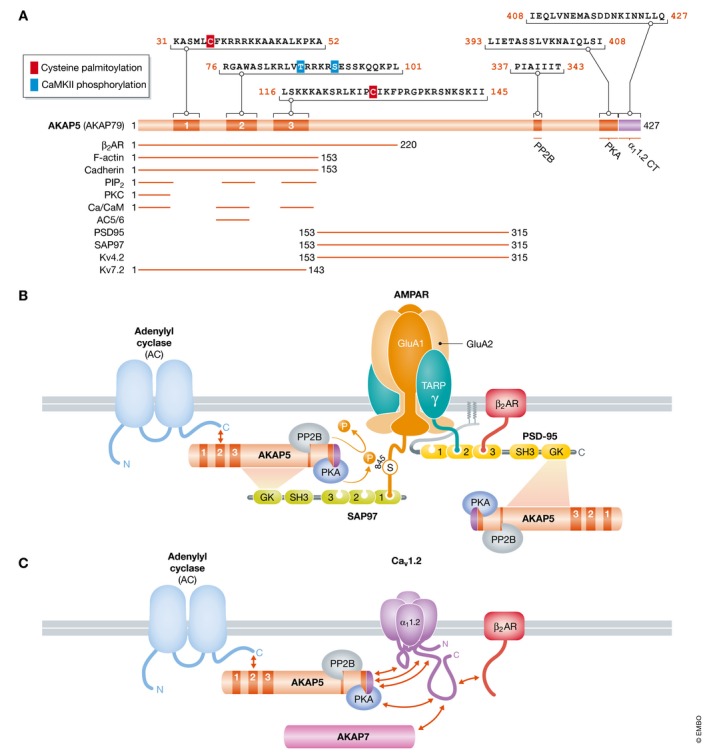
(A) Overview of AKAP5 binding partners and their binding sites. Residue numbering refers to human AKAP79. The N‐terminus is formed by three segments designated A, B, and C. These segments are polybasic regions, each of which can bind to Ca2+/CaM and PIP2. In addition, PKC binds to A and adenylyl cyclases 5 and 6 (AC5/6) bind via their N‐termini to B. PP2B binds to a PIXIT‐like motif near the center of AKAP5 and PKA to a motif that is about 20 residues upstream of the very C‐terminus. Immediately downstream of the PKA site is a leucine zipper‐like motif that binds to a leucine zipper‐like motif near the C‐terminus of the Cav1.2 α11.2 subunit. PSD‐95 and SAP97 interact through their SH3 and GK domains with a broad region in the center of AKAP5, which also binds to KV4.2. Other binding sites are less clearly defined. The two palmitoylation sites are identified by red squares and the two known CaMKII phosphorylation sites by blue squares. (B) The β2 AR–AMPAR complex. AC binds to the N‐terminus, PP2B to the middle region, and PKA to the C‐terminus of AKAP5, which is connected with AMPARs via SAP97, which binds to the very C‐terminus of GluA1 (Leonard et al, 1998; Tavalin et al, 2002; Zhang et al, 2013). The β2 AR binds to the third PDZ domain of PSD‐95, which is linked to AMPARs via TARPs (γ), which bind with their very C‐termini to the second and, with lower affinity, also first and third PDZ domains of PSD‐95 (Hafner et al, 2015). PSD‐95 might recruit a second AKAP5/PKA/PP2B complex. PKA and PP2B mediate phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of S845 on GluA1, respectively. (C) The β2 AR directly binds to the C‐terminus of α11.2. AKAP5 binds to three different regions as depicted (red arrows); the leucine zipper‐like segment near C‐terminus of α11.2 also binds alternatively AKAP7. AKAP5 recruits PKA, PP2B, and likely ACs to the Cav1.2 complex.
