Figure 9. Hypothetical postsynaptic AMPAR regulation and trapping by CaMKII .
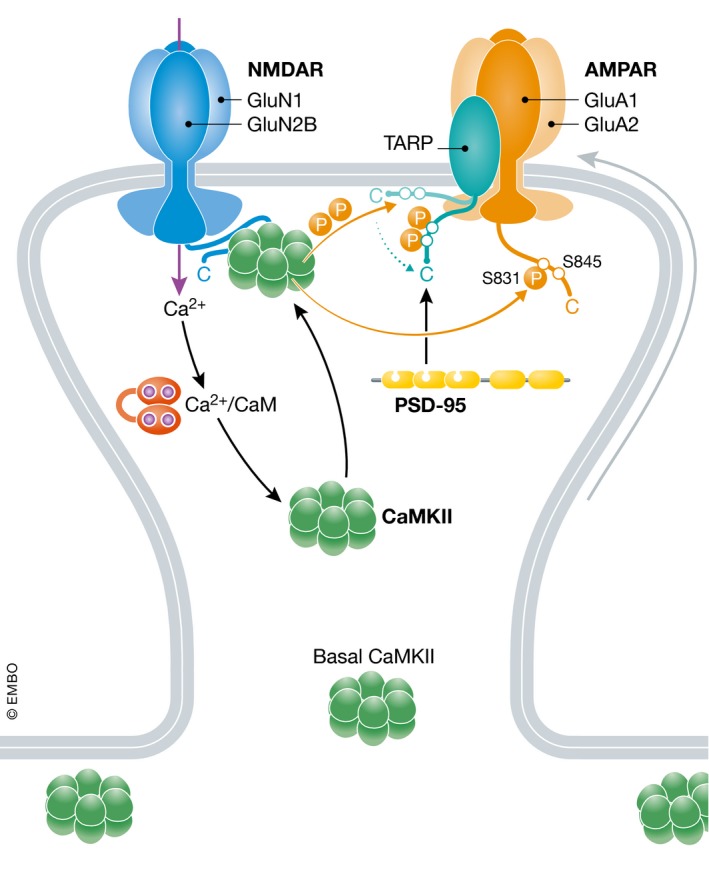
AMPARs reach the postsynaptic density by lateral diffusion. Ca2+ influx via the NMDA receptor will lead to activation of CaMKII by Ca2+/CaM. The immediate autophosphorylation on T286 causes binding of CaMKII to the GluN2B C‐terminus, which is important for phosphorylation of postsynaptic proteins (Halt et al, 2012). Phosphorylation of GluA1 on S831 increases channel activity. The Ca2+ influx also augments detachment of the TARP C‐termini from the cytosolic face of the plasma membrane, which are then phosphorylated by CaMKII. Phosphorylation of either γ2 or γ8 will increase their binding to PSD‐95 to trap AMPARs. Recruitment of CaMKII to postsynaptic sites that are activated during LTP is likely part of the mechanism that ensures synapse specificity of LTP (Hell, 2014).
