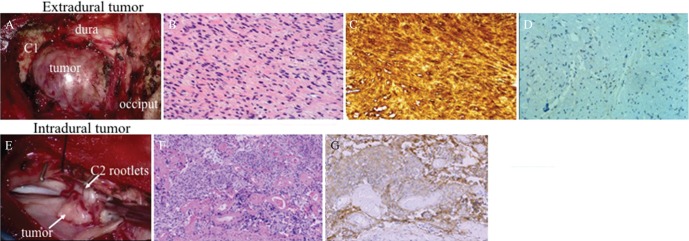
Fig. 2.
(A) Intraoperative photograph showing the extradural tumor compressing the dural theca between the occiput and C1. (B) Histopathological examination of the extradural tumor via H&E staining showed compactly arranged proliferation of spindle cells with occasional nuclear palisading and loosely arranged cells with round to oval hyperchromatic nuclei. (C) Immunohistochemical study showed that the tumor cells were diffusely positive for S-100 protein. These findings were consistent with histological characteristics of schwannoma. (D) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was weakly and focally expressed around the vessels. (E) Intraoperative image showed that the intradural tumor was attached to the dura and involved several C2 rootlets. (F) Histopathological examination of the intradural tumor via H&E staining showed that it consists of the nest of meningothelial cells and psammoma bodies. (G) Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells were positive for epithelial membrane antigen. These histological features were in accordance with the histopathological characteristic of meningioma.