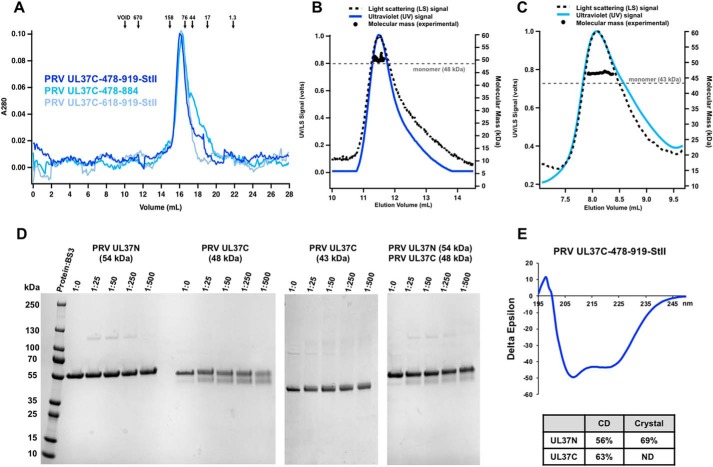
Figure 2.
Biochemical and biophysical characterization of PRV UL37C. A, PRV UL37C(478–919)-StII (royal blue), PRV UL37C(478–884) (medium blue), and PRV UL37C(618–919)-StII (pale blue) with standard proteins (arrows) analyzed by SEC. Standardization using elution volumes, molecular masses of the standard proteins, and column specifics yielded a standard curve for molecular mass estimations for PRV UL37C. B, SEC-MALS of PRV UL37C(478–919)-StII; C, PRV UL37C(478–884) in solution. The signal from the 90° scattering detector is shown as a dashed line, and the signal from the UV absorbance is shown in color. Experimental molecular masses are plotted as black dots against the right y axis, as calculated across the protein elution peak. Theoretical molecular masses corresponding to those of a monomer are indicated as horizontal dashed gray lines. D, BS3 chemical cross-linking of PRV UL37N (54 kDa), PRV UL37C(478–919)-StII (48 kDa), and PRV UL37C(478–884) (43 kDa). Gels were split to hide unrelated lanes, but contrast settings and molecular weight ladder remain consistent between gel sections. E, CD of PRV UL37C(478–919)-StII. Helical content from UL37C was estimated by the K2D2 program (http://k2d2.ogic.ca/) using the spectrum over the range from 190 to 240 nm. Helical content from UL37N was reported previously (27).