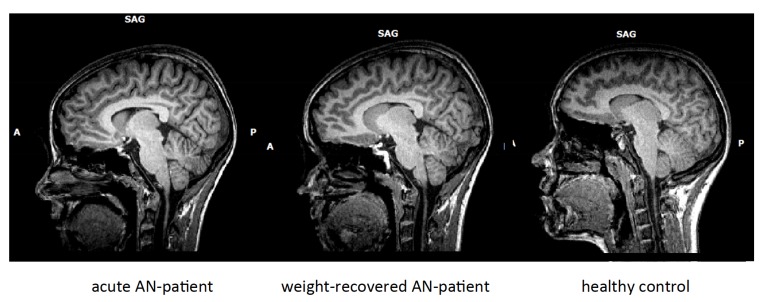
Fig. (1).
From left to right: T1-weighted sagittal MRI pictures of a female patient with acute anorexia nervosa (AN), the same patient short-term weight-recovered and a healthy control subject. Note that the external and internal cerebro-spinal fluid cavities are enlarged, most prominently in the acutely ill patient with AN.