Fig. 1.
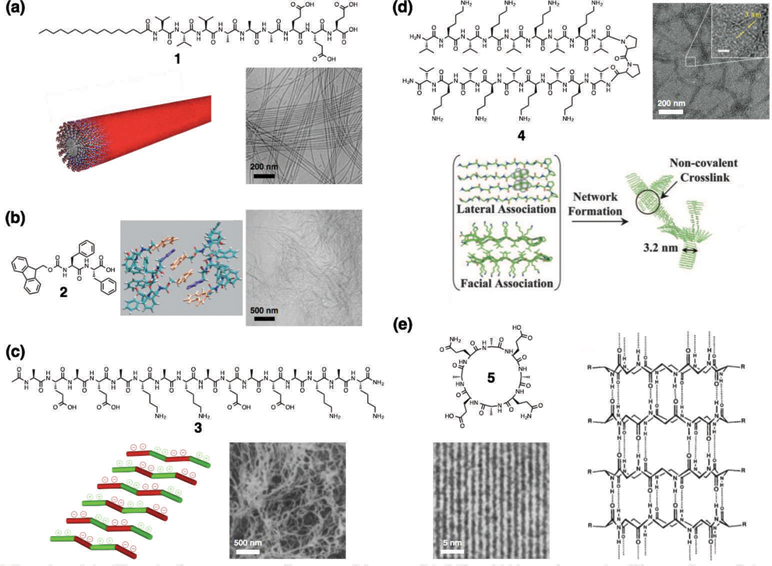
(a) Chemical structure of a peptide amphiphile (PA), schematic illustration of its supramolecular assembly into a cylindrical nanofiber, and cryogenic transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM) of nanofibers. Reprinted with permission from ref. 32 (Copyright 2015 Wiley-VCH). (b) Chemical structure of an Fmoc-dipeptide, schematic illustration of molecular packing (Fmoc groups: orange, phenyl groups: purple), and cryogenic scanning electron microscopy (cryo-SEM) of nanofibers. Reprinted with permission from ref. 15 (Copyright 2008 Wiley-VCH). (c) Chemical structure of the Z-DNA-binding mimetic amphipathic peptide, schematic illustration of its supramolecular assembly, and SEM of nanofibers. Reprinted with permission from ref. 16 (Copyright 1993 National Academy of Sciences). (d) Chemical structure of a β-hairpin peptide, schematic illustration of its folding and supramolecular assembly, and TEM of nanofibers. Reprinted with permission from ref. 19 (Copyright 2007 National Academy of Sciences). (e) Chemical structure of a cyclic peptide with alternating d- and l-amino acids and its tubular assembly, and TEM of closely packed nanotubes. Reprinted with permission from ref. 21 (Copyright 1993 Nature Publishing Group).
