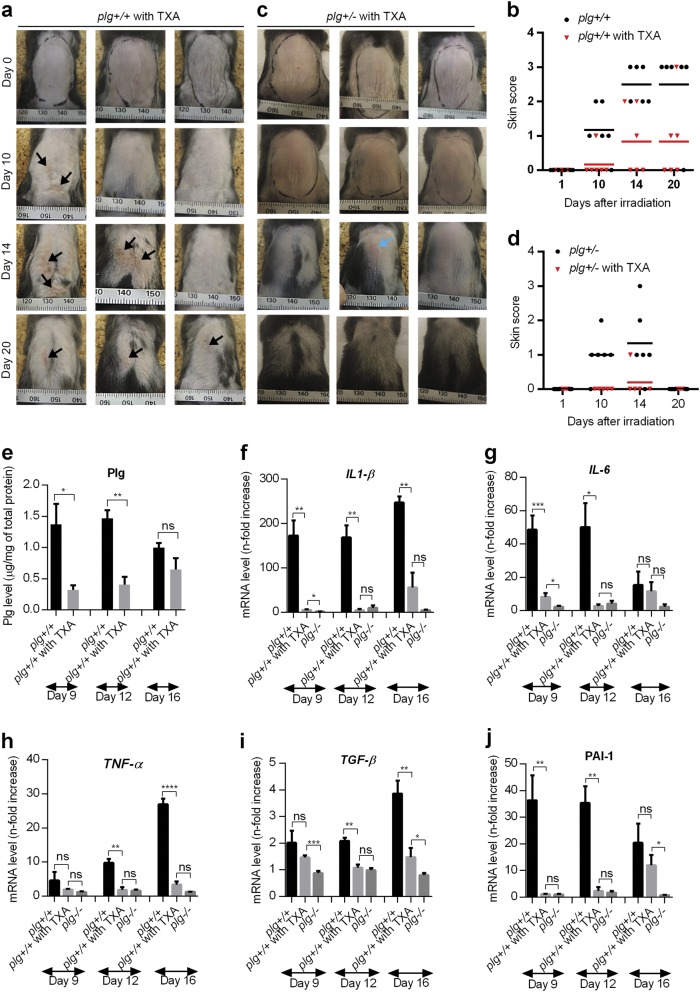
Fig. 6. Tranexamic acid inhibits the development of radiodermatitis in plg+/+ and plg+/− mice.
plg+/+ and plg+/− mice were treated with TXA in their drinking water from 2 days before irradiation until day 10 post irradiation. Control mice were irradiated but did not receive TXA. a, b Representative photographs of the dorsal skin of irradiated plg+/+ mice treated with TXA, and a comparison of the quality of the dorsal skin in irradiated control and TXA-treated plg+/+ mice (n = 6 per time point). c, d Representative photographs of the dorsal skin of irradiated plg+/− mice treated with TXA, and a comparison of the quality of the dorsal skin in irradiated control and TXA-treated plg+/− mice (n = 6 per time point). Arrows show the wounded skin area. e Plasminogen levels in the skin extracts of control and TXA-treated plg+/+ mice on different days after irradiation. f–j RT-PCR measurement of mRNA levels of IL1-β (f), IL-6 (g), TNF-α (h), TGF-β (i), and PAI-1 (j) in the irradiated skin of control and TXA-treated plg+/+ and in plg−/− mice on different days after irradiation. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005; ****P < 0.001.